110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

泛素化因子 E4B(UBE4B)在肾细胞癌患者术后的预后以及肾肿瘤细胞生长和转移中的作用
Authors Huang XQ, Hao S, Zhou ZQ, Huang B, Fang JY, Tang Y, Zhang JH, Xia JC
Received 2 September 2019
Accepted for publication 24 December 2019
Published 8 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 185—197
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S229577
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Object: This study aimed at investigating the clinical significance and biological function of ubiquitination factor E4B (UBE4B) in human renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
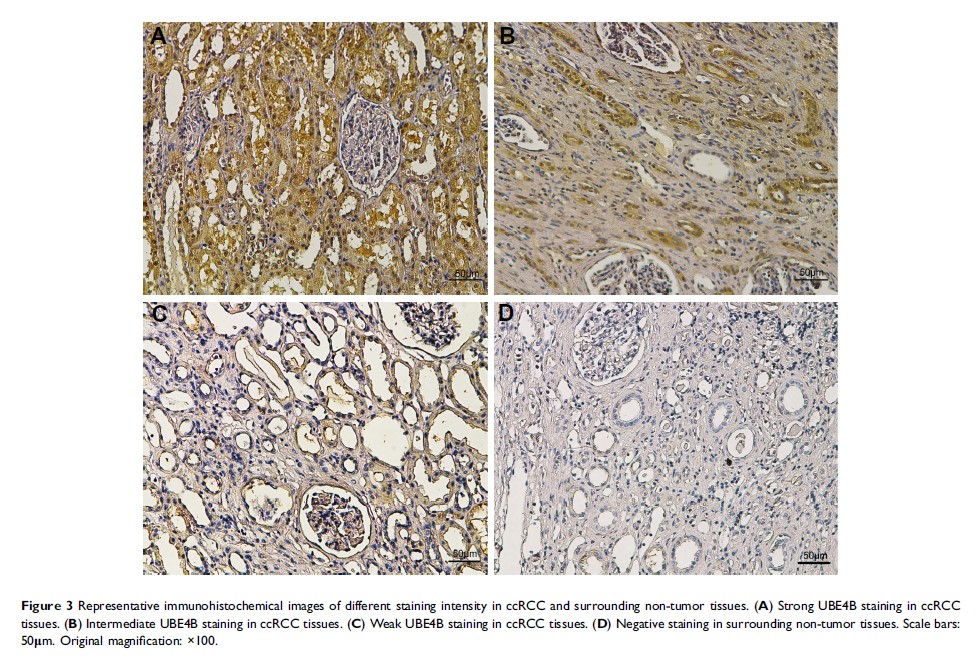
Methods: 19 paired clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) tumor samples and the matched neighboring non-tumor samples were used to detect the expression of UBE4B in RCC tumor by Western blotting and RT-qPCR. UBE4B expression was also detected in 151 ccRCC paraffin-embedded tumor samples by using immunohistochemistry. Overall survival (OS) in different UBE4B expression groups were compared with Log rank test. The prognostic value of UBE4B expression in OS was evaluated with the univariate and multivariate Cox regression models. UBE4B was knocked down by small interfering RNA (siRNA) technology, and the effect of UBE4B on cell proliferation, colony formation, metastasis, apoptosis and cell cycle of RCC cells were examined in vitro.
Results: Both protein and mRNA levels of UBE4B were up-regulated in ccRCC tumor tissues in contrast to the corresponding adjacent nontumor ones. UBE4B expression was positively associated with tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage and distant metastasis in ccRCC patients. Survival analyses indicated that low expression of UBE4B was associated with increased OS in ccRCC patients. Functional analyses demonstrated that siRNA silencing of UBE4B expression in SKRC39 and ACHN cells further reduced the growth, motility and invasiveness of RCC cells. Moreover, siRNA silencing of UBE4B in the RCC cell lines did not induce apoptosis, and an increase in the cell population was observed during the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle.
Conclusion: UBE4B might act as an oncogene in regulating RCC development. Therefore it could be served as an effective indicator to predict OS and a potential biomarker for targeted therapy of RCC patients.
Keywords: renal cell carcinoma, UBE4B, prognosis, oncogene