110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在实践中,采用以程序性细胞死亡蛋白-1(PD-1)为靶点的免疫疗法治疗晚期肝细胞癌
Authors Cui H, Dai G, Guan J
Received 16 October 2019
Accepted for publication 16 December 2019
Published 8 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 143—149
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234868
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant solid tumors. Its incidence is increasing worldwide due to the dissemination of hepatitis B infection, HCV infection and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-related HCC. For patients with advanced HCC, the available treatments are extremely limited and the prognosis is very poor. Therefore, it is urgent to discover new innovative approaches. Programmed cell death protein-1-targeted immunotherapy has shown promising results in multicenter clinical trials.
Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of anti-PD-1 agent in patients with advanced primary hepatocellular carcinoma.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 55 patients with advanced primary hepatocellular carcinoma who had been administered anti-PD-1 agent. Tumor response was assessed according to the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors and any adverse events were recorded.
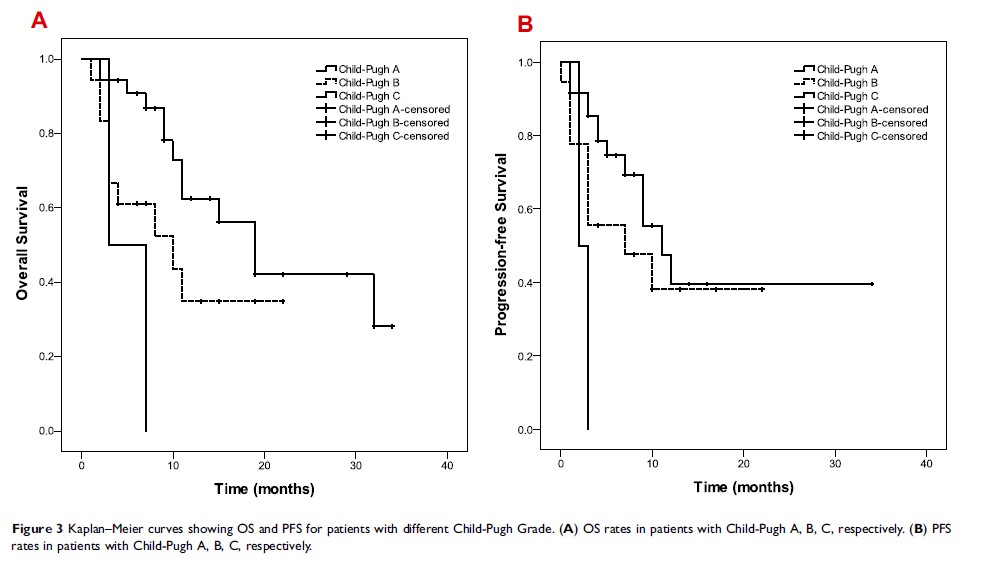
Results: The median overall survival (OS) was 15 months. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 10 months. No patient had complete response (CR) and 12 (22%) participants achieved partial response (PR), resulting in an overall response rate (ORR) of 22%. Thirty-seven (67%) patients showed stable disease (SD) and 6 (11%) subjects had progressive disease (PD) at first radiological evaluation. The disease control rate (DCR) was 89%. The total side effect rate was 61.8% and most were relieved after treatment.
Conclusion: Programmed cell death protein‐1‐targeted immunotherapy is a safe and effective treatment for advanced primary hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, programmed cell death protein-1-targeted immunotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitor, adverse events