110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

姜黄素通过激活 Nrf2 信号通路减轻奥沙利铂引起的肝损伤和氧化应激
Authors Lu Y, Wu S, Xiang B, Li L, Lin Y
Received 23 July 2019
Accepted for publication 13 December 2019
Published 9 January 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 73—85
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S224318
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Purpose: Oxaliplatin (OXA)-induced liver injury is one of the main limiting factors affecting the efficacy of OXA-based chemotherapy in patients with colorectal liver metastases. In addition, oxidative stress is an important pathophysiological mechanism of OXA-induced liver injury. Therefore, dietary antioxidants may decrease or prevent hepatic toxicity in vivo and be beneficial to OXA-based chemotherapy.
Methods: An experimental OXA-induced liver injury animal model was established, and the protective effects of curcumin (CUR) against OXA-induced liver injury were investigated. ELISA was used to determine the levels of MDA, SOD, CAT, and GSH in liver tissue. The effect of CUR treatment on the expression of cytokines and the Nrf2 pathway was determined by real-time PCR and Western blotting.
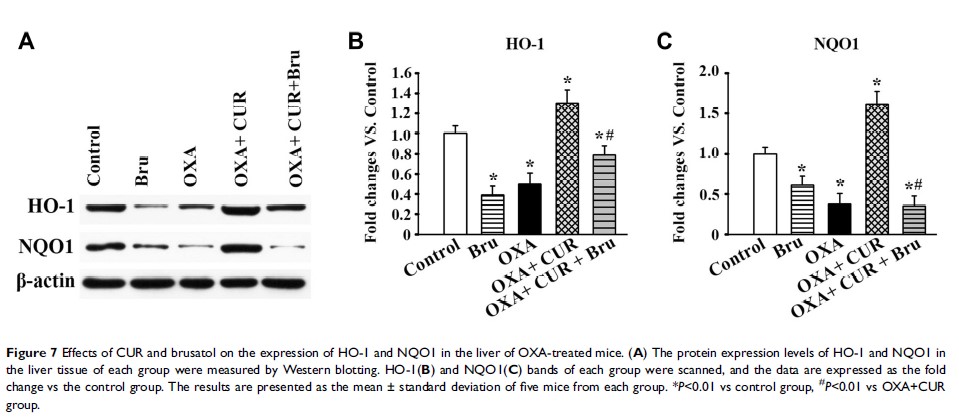
Results: CUR treatment alleviated OXA-induced hepatic pathological damage and splenomegaly. The protective effect of CUR was demonstrated to be correlated with inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation, and the coagulation system. Furthermore, Western blotting revealed that CUR treatment reverses the suppression of Nrf2 nuclear translocation and increases the expression of HO-1 and NOQ1 in mice with OXA-induced liver injury. Moreover, the Nrf2 activation and hepatoprotective effect of CUR were abolished by brusatol.
Conclusion: Curcumin attenuates oxaliplatin-induced liver injury and oxidative stress by activating the Nrf2 pathway, which suggests that CUR may be potentially used in the prevention and treatment of OXA-induced liver injury.
Keywords: oxaliplatin, curcumin, liver injury, oxidative stress, Nrf2