110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

岩白菜素通过 PPAR-γ 信号通路抑制炎症因子的释放、细胞凋亡和自噬,从而发挥保护肝作用
Authors Xiang S, Chen K, Xu L, Wang T, Guo C
Received 28 August 2019
Accepted for publication 6 January 2020
Published 13 January 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 129—143
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S229063
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
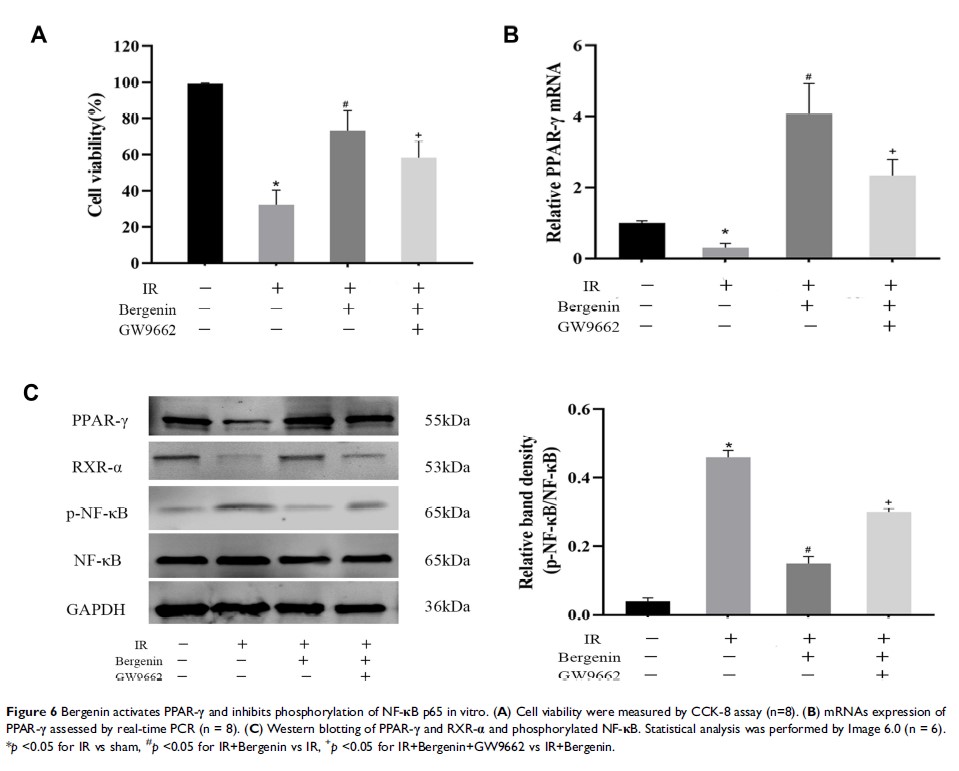
Objective: Hepatic ischemia reperfusion (IR) limits the development of liver transplantation technology. The aim of this study was to explore the protective effects of Bergenin on hepatic IR, particularly the elimination of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activation of the peroxisome proliferators activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ) pathway.
Methods: Initial experiments were performed to confirm the non-toxicity of Bergenin. Mice were randomly divided into sham, IR, and IR + Bergenin (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) groups, and serum and tissue samples were obtained at 2, 8 and 24 h for detection of liver enzymes (ALT and AST), inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β), ROS, cell death markers (Bcl-2, Bax, Beclin-1 and LC3) and related important pathways (PPAR-γ, P38 MAPK, NF-κB p65 and JAK2/STAT1).
Results: Bergenin reduced the release of ROS, down-regulated inflammatory factors, and inhibited apoptosis and autophagy. Additionally, expression of PPAR-γ-related genes was increased and phosphorylation of P38 MAPK, NF-κB p65 and JAK2/STAT1-related proteins was decreased in Bergenin pre-treatment groups in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Bergenin exerts hepatic protection by eliminating ROS, affecting the release of inflammatory factors, and influencing apoptosis- and autophagy-related genes via the PPAR-γ pathway in this model of hepatic IR injury.
Keywords: hepatic ischemia reperfusion, Bergenin, reactive oxygen species, apoptosis, autophagy