110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

预测结肠直肠癌分子表型的线型图
Authors Yu Z, Yu H, Zou Q, Huang Z, Wang X, Tang G, Bai L, Zhou C, Zhuang Z, Xie Y, Wang H, Xu G, Chen Z, Fu X, Huang M, Luo Y
Received 13 October 2019
Accepted for publication 24 December 2019
Published 13 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 309—321
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234495
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with different molecular phenotypes, including microsatellite instability (MSI), CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP), and somatic mutations in BRAF and KRAS gene, vary in treatment response and prognosis. However, molecular phenotyping under adequate quality control in a community-based setting may be difficult. We aimed to build the nomograms based on easily accessible clinicopathological characteristics to predict molecular phenotypes.
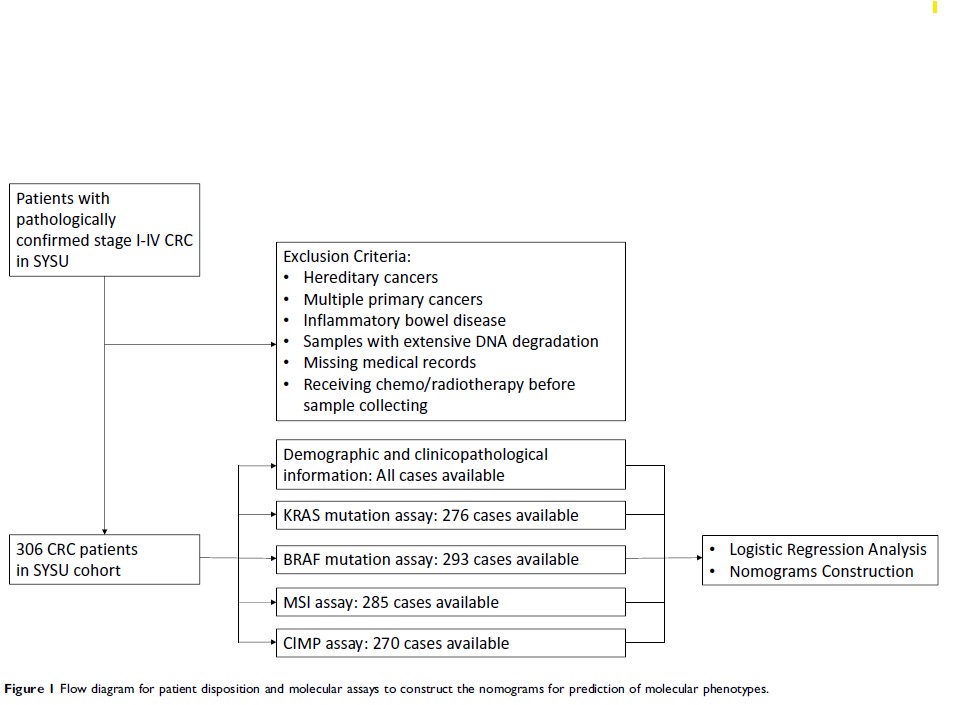
Methods: Three hundred and six patients with pathologically confirmed stage I-IV CRC were included in the cohort. The assays for MSI, CIMP, and mutations in BRAF and KRAS gene were performed using resected tumor samples. The candidate predictors were identified from clinicopathological variables using multivariate Logistic regression analyses to construct the nomograms that could predict each molecular phenotype.
Results: The incidences of MSI, CIMP, BRAF mutation and KRAS mutation were 25.3% (72/285), 2.5% (7/270), 3.4% (10/293), and 34.8% (96/276) respectively. In the multivariate Logistic analysis, poor differentiation and high neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were independently associated with MSI; poor differentiation, high NLR and high carcinoembryonic antigen/tumor size ratio (CSR) were independently associated with CIMP; poor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion and high CSR were independently associated with BRAF mutation; poor differentiation, proximal tumor, mucinous tumor and high NLR were independently associated with KRAS mutation. Four nomograms for MSI, CIMP, BRAF mutation and KRAS mutation were developed based on these independent predictors, the C-indexes of which were 61.22% (95% CI: 60.28– 62.16%), 95.57% (95% CI: 95.20– 95.94%), 83.56% (95% CI: 81.54– 85.58%), and 69.12% (95% CI: 68.30– 69.94%) respectively.
Conclusion: We established four nomograms using easily accessible variables that could well predict the presence of MSI, CIMP, BRAF mutation and KRAS mutation in CRC patients.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, microsatellite instability, CpG island methylator phenotype, BRAF , KRAS , nomogram, prediction of molecular subtypes