110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

急性中风患者血清中的外泌体长非编码 RNA 表达
Authors Xu X, Zhuang C, Chen L
Received 9 September 2019
Accepted for publication 23 December 2019
Published 13 January 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 153—160
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S230332
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
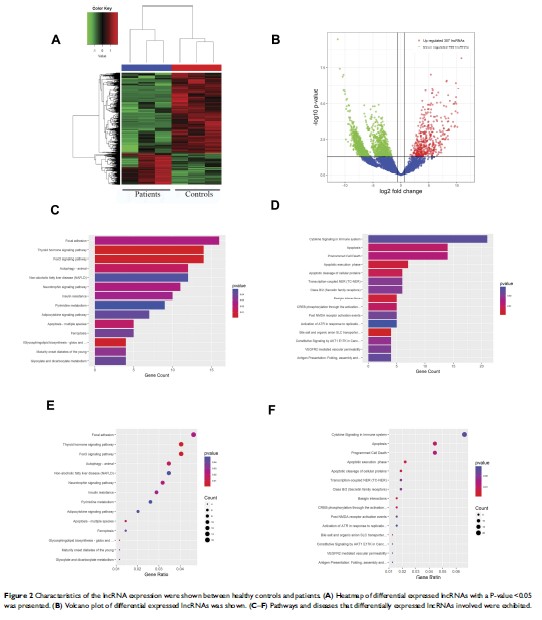
Background: Acute minor stroke (AMS) is one kind of hypoxic ischemic necrosis with no more than 4 National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score. However, the early diagnosis of AMS is tough for lack of effective molecular markers. Recently, many long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) associated with AMS have been gradually revealed. Here, we aim to find the potential biomarkers of lncRNAs in exosomes isolated from blood serum of patients with AMS for early detection.
Methods: RNA-seq technique, KEGG pathway analysis and GO enrichment analysis were used in this study. Besides, reverse transcription real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to validate expression levels of four of eleven differentially expressed lncRNAs (lnc-CRKL-2, lnc-NTRK3-4, RPS6KA2-AS1 and lnc-CALM1-7) involved in the neurotrophin signaling pathway.
Results: The expression levels of lnc-CRKL-2 (mean value 48, standard deviation 4.583, P = 0.003) and lnc-NTRK3-4 (mean value 32.3, standard deviation 2.08, P = 0.001) were increased significantly in AMS patients, while the expression levels of RPS6KA2-AS1 (mean value − 118.7, standard deviation 7.09, P = 0.001) and lnc-CALM1-7 (mean value − 148.7, standard deviation 6.10, P = 0.001) were decreased dramatically.
Conclusion: In conclusion, these four new revealed lncRNAs may be used as novel joint biomarkers for the early detection of AMS.
Keywords: exosomes, stroke, LncRNAs, biomarker