110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:纳米材料诱导的光热疗法与化学疗法、自噬抑制作用相结合可逆转胆囊癌的进展
Authors Cai Q, Wang X, Wang S, Jin L, Ding J, Zhou D, Ma F
Received 17 September 2019
Accepted for publication 2 January 2020
Published 15 January 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 253—262
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S231289
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
***本文章已被撤回***
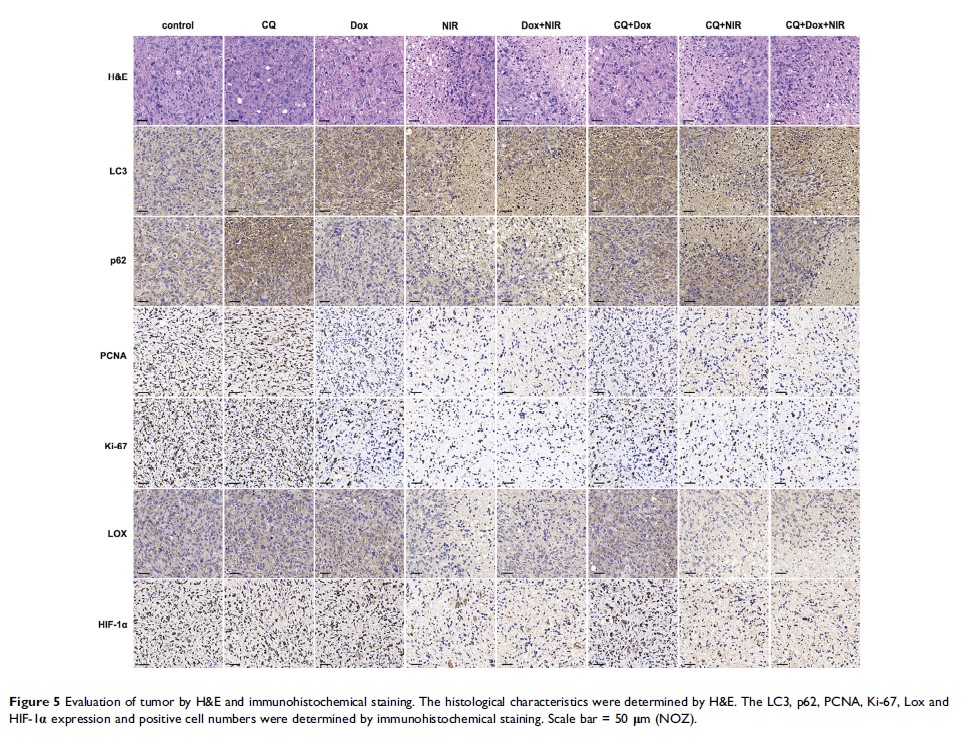
Introduction: Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is the most common malignancy in biliary tract with extremely poor prognosis. Photothermal therapy (PTT) shows great promises for tumor therapy, which causes tumor cell death via selectively directed heating released by nanoparticles under the near-infrared irradiation. Through degrading damaged organelles and misfolded proteins in autophagosomes, autophagy plays a vital role in maintaining the intracellular homeostasis. The present study attempted to combine chemotherapy and autophagy blocking with PTT.
Materials and Methods: We purchased multi-walled carbon nanotubes from Nanostructured and Amorphous Materials and performed PTT using an 808-nm diode laser. The cytotoxic effects of PTT and chemotherapy in vitro were assessed by cell viability analysis. The effects of PTT and chemotherapy on autophagy in vitro were assessed by GFP-LC3 and Western blot. And these results were confirmed by in vivo experiment.
Results: Both PTT and chemotherapy could trigger cytoprotective autophagy to tolerate the cellular stresses and prolong the survival of GBC cell; therefore, the blocking of autophagy could enhance the efficacy of PTT and chemotherapy in GBC treatment in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin and autophagy inhibitor chloroquine could enhance the efficacy of nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia in GBC.
Keywords: gallbladder cancer, photothermal therapy, carbon nanotubes, chemotherapy, autophagy