110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

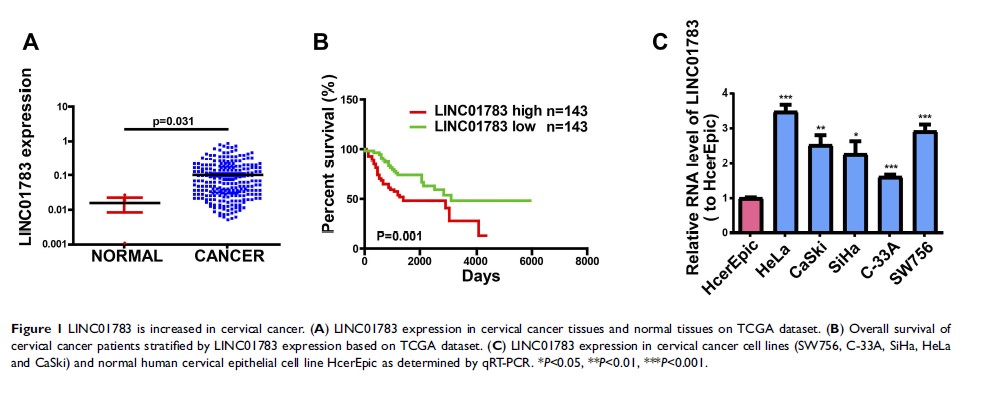
长非编码 RNA LINC01783 通过使 miR-199b-5p 海绵化来介导 GBP1,从而促进宫颈癌的进展
Authors Chen W, Xiong L, Yang L, Yang L, Li L, Huang L, Liang X, Xue J, Tan B
Received 7 September 2019
Accepted for publication 1 November 2019
Published 16 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 363—373
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S230171
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Background: Long non-coding RNA showed potential regulating effects in oncogenesis. Highly expressed LncRNA LINC01783 is observed in cervical cancer. However, the specific pathogenesis of cervical cancer is still unclear.
Methods: Differential lncRNAs in cervical cancer were identified based on TCGA dataset. Subsequently, qRT-PCR was utilized for testing the LINC01783 expression in cervical cancer cell lines and normal human cervical epithelial cell line HcerEpic. CCK-8, EdU, Wound healing assay, Transwell assay and flow cytometry were used for detecting proliferative and migratory potential, cell cycle and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells, respectively. To identify the potential target of LINC01783, bioinformatics assay and dual-luciferase reporter gene assay were performed. Moreover, to clarify their interactions and roles in regulating the progression of cervical cancer, Western blot assay and RIP assay were carried out.
Results: Our results revealed LINC01783 is overexpressed in cervical cancer cells. Overexpressed LINC01783 considerably accelerated the cell proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells while restrained cell apoptosis of them. Moreover, LINC01783 positively regulated the GBP1 expression via competitively binding to miR-199b-5p.
Conclusion: LINC01783 is involved in the progression of cervical cancer through competitively binding to miR-199b-5p to mediate GBP1 expression.
Keywords: cervical cancer, LncRNA, ceRNA, proliferation, migration, invasion