110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

三氧化二砷/硼替佐米/抗坏血酸/地塞米松(ABCD)方案与硼替佐米/地塞米松(BD)方案在新诊断的骨髓瘤患者的诱导和合并化疗中的效率和耐受性对比
Authors Qian W, Wang L, Li P, Hu Y, Wang Q, Yi K, Wu M, Xu Y, Song J, Chen P, Zhang H, Ma J, Xie Y
Received 16 April 2019
Accepted for publication 5 November 2019
Published 20 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 431—441
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S212455
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Purpose: This study was aimed at comparing the efficacy and tolerability of an arsenic trioxide/bortezomib/ascorbic acid/dexamethasone (ABCD) regimen with efficacy and tolerability of a bortezomib/dexamethasone (BD) regimen in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma.
Patients and Methods: Fifty-seven and sixty-four patients were treated with the ABCD and BD regimens, respectively. Eligible and agreeable patients received autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation followed by consolidation.
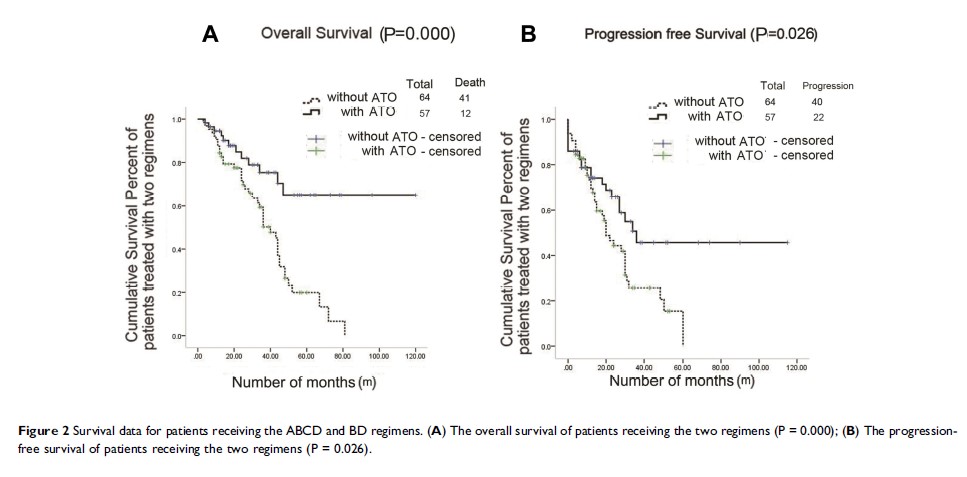
Results: The response rates (above VGPR) were 74.1% and 32.8% in the ABCD- and BD-treated groups, respectively (P = 0.000). Compared to BD regimen, ABCD regimen significantly improved PFS (P = 0.026) and OS (P = 0.000) in newly diagnosed patients. Patients with a high tumor burden, low or standard risk, and without auto-HSCT seemed to especially benefit compared to the same group with BD regimen. ABCD also showed better tolerability with lower bone marrow suppression (P = 0.026). Furthermore, complete response or near CR after induction therapy was a good prognostic factor for ABCD-associated OS and PFS.
Conclusion: ABCD is an effective and tolerable regimen compared with BD regimen in newly diagnosed myeloma patients. ABCD regimen could be an economical, effective, and tolerable choice in low- and standard-risk patients.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, arsenic trioxide, bortezomib, overall survival, treatment response