110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA-ATB 通过靶向 miR-204-3p 促进卵巢癌的肿瘤发生
Authors Yuan D, Qian H, Guo T, Ye J, Jin C, Liu X, Jiang L, Wang X, Lin M, Yu H
Received 10 September 2019
Accepted for publication 22 December 2019
Published 20 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 573—583
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S230552
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Ovarian cancer ranks fifth among the most prevalent cancer type in females all over the world. It is the second most frequent malignant tumor which accounts for 3% of cancer in females. Therefore, to explore the mechanism of carcinogenesis in ovarian cancer is important to develop new treatment methods. It has been previously found that lncRNA-ATB could promote the tumorigenesis of malignant tumors. However, the role of lncRNA-ATB during the progression of ovarian cancer remains unclear.
Methods: Gene expressions in tissues or cells were detected by using qRT-PCR. Western blot was performed to investigate the protein expressions in ovarian cancer cells. Cell apoptosis was tested by flow cytometry. Moreover, the correction between lncRNA-ATB and miR-204-3p was examined by Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA pulldown. Cell proliferation and invasion were detected by CCK-8, Ki-67 staining and transwell assay, respectively. Finally, xenograft mice model was established to confirm the result of in vitro experiments.
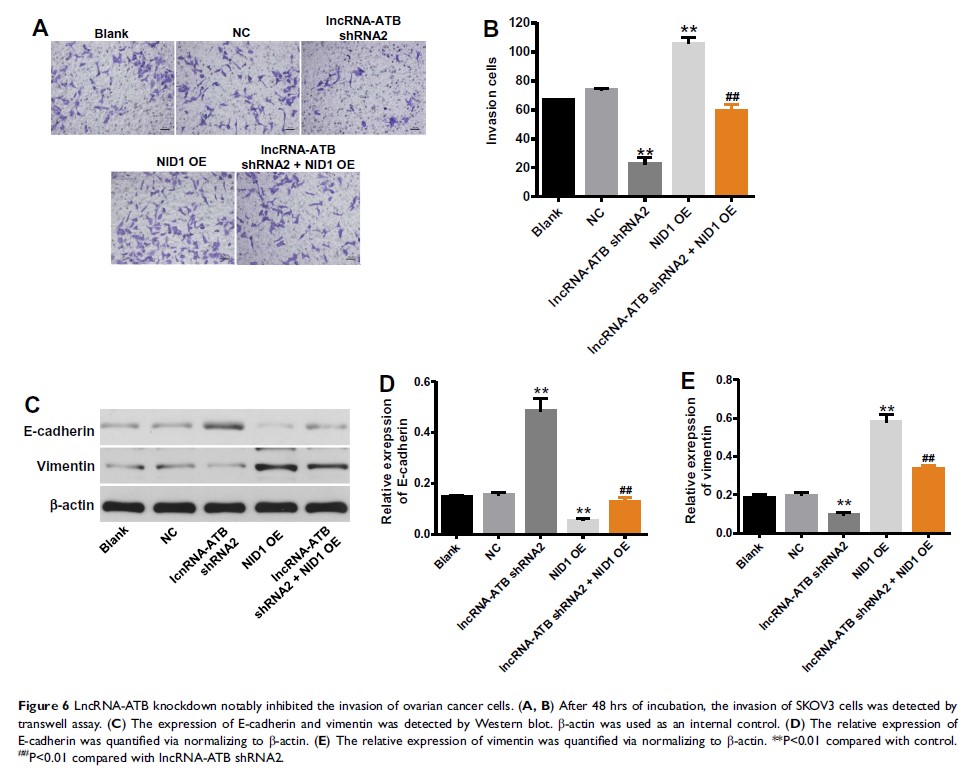
Results: LncRNA-ATB silencing significantly inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells. In addition, luciferase activity suggested that lncRNA-ATB negatively regulated miR-204-3p in ovarian cancer. Besides, Nidogen 1 (NID1) was the direct target of miR-204-3p. Overexpression of NID1 could notably reverse the inhibitory effect of lncRNA-ATB knockdown on the progression of ovarian cancer. Finally, lncRNA-ATB silencing notably attenuated the severity of ovarian cancer in vivo.
Conclusion: Downregulation of lncRNA-ATB significantly inhibited the tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo, which may serve as a potential novel target for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: ovarian cancer, lncRNA-ATB, miR-204-3p, NID1