110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在理解伊维菌素抗肿瘤作用分子机制方面的进展
Authors Liu J, Zhang K, Cheng L, Zhu H, Xu T
Received 5 November 2019
Accepted for publication 30 December 2019
Published 21 January 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 285—296
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S237393
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
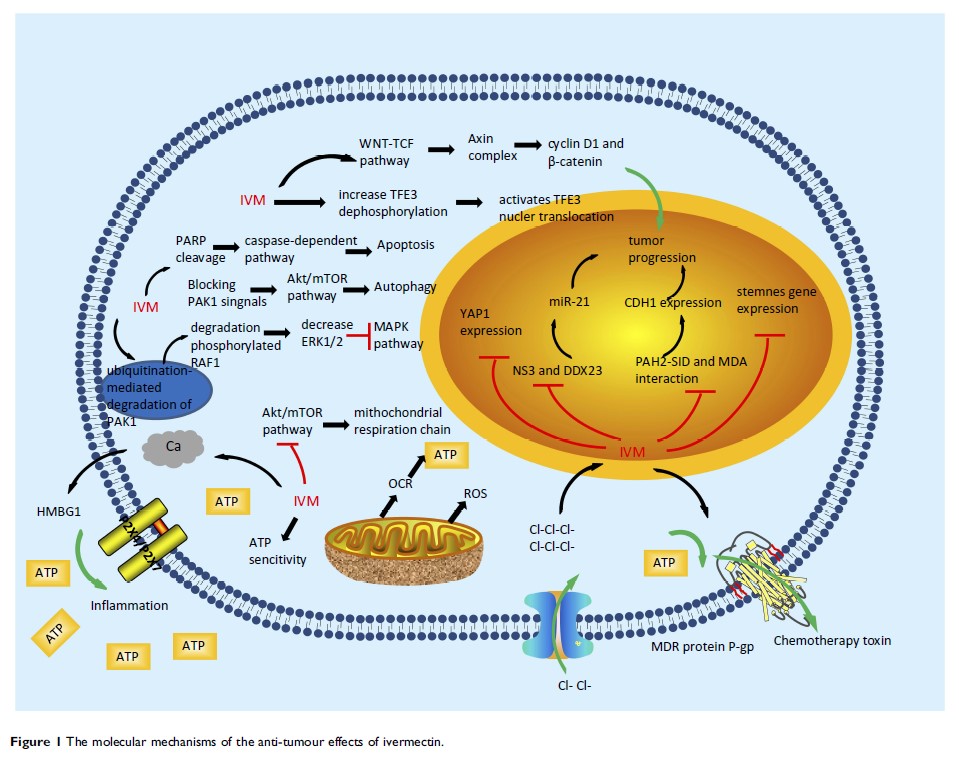
Abstract: Ivermectin, a dihydro derivative of avermectin (AVM), was introduced into the veterinary, agricultural and aquaculture markets for animal health in 1981. Ivermectin was soon adopted in 1987 as a human medicine that was originally used for the treatment of onchocerciasis, a parasitic infection. Since then, ivermectin has also been used to control other human diseases and has exerted a significant effect on human health and welfare. In the past decade, many published studies have attempted to determine the role of ivermectin in cancer. In this review, we summarize the published studies to define the current progress in the characterization of ivermectin. Ivermectin causes cell death in cancer cell lines by inducing PAK1-mediated cytostatic autophagy, caspase-dependent apoptosis and immunogenic cell death (ICD) through the modulation of some pathways, including the WNT-T cell factor (TCF), Hippo and Akt/mTOR pathways. Ivermectin can affect the growth and proliferation of cancer cells and plays several different roles, such as its functions as an RNA helicase, a small-molecule mimetic of the surface-induced dissociation (SID) peptide, an activator of chloride channel receptors, and an inducer of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. In addition, ivermectin induces the multidrug resistance protein (MDR), has potent anti-mitotic activity, targets angiogenesis and inhibits cancer stem-like cells (CSCs). Many studies have proven that ivermectin exerts antitumour effects and might thus benefit patients with cancer after sufficient clinical trials.
Keywords: ivermectin, cancer, molecular mechanisms, antitumour effects, drug therapy