110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Cosmc 中断介导的 O-糖基化异常可通过 CD44 受损来抑制乳腺癌细胞生长
Authors Du T, Jia X, Dong X, Ru X, Li L, Wang Y, Liu J, Feng G, Wen T
Received 15 October 2019
Accepted for publication 3 January 2020
Published 22 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 511—522
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S234735
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
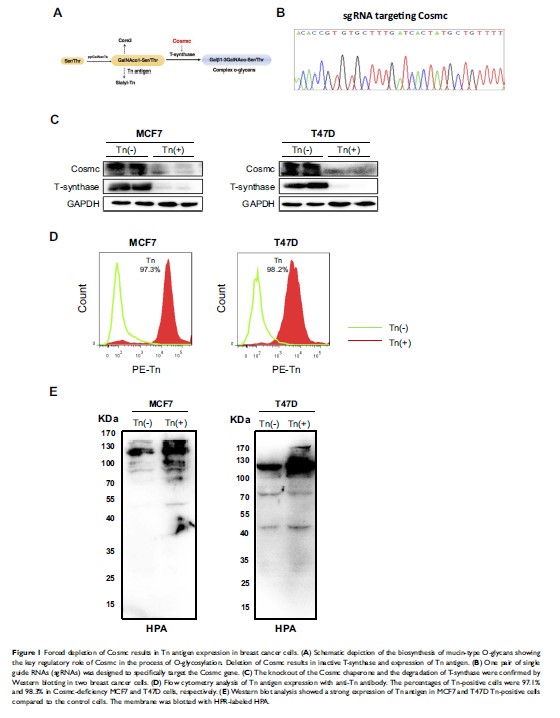
Background: Breast cancer remains the most lethal malignancy in women worldwide. Aberrant O-glycosylation is closely related to many human diseases, including breast carcinoma; however, its precise role in cancer development is insufficiently understood. Cosmc is an endoplasmic reticulum-localized chaperone that regulates the O-glycosylation of proteins. Cosmc dysfunction results in inactive T-synthase and expression of truncated O-glycans such as Tn antigen. Here we investigated the impact of Cosmc disruption-mediated aberrant O-glycosylation on breast cancer cell development through in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Materials and Methods: We deleted the Cosmc gene in two breast cancer cell lines (MCF7, T47D) using the CRISPR/Cas-9 system and then measured the expression levels of Tn antigen. The proliferation of Tn-positive cells was examined by RTCA, colony formation and in vivo experiments. The effects of Cosmc deficiency on glycoprotein CD44 and MAPK pathway were also determined.
Results: Both in vitro and in vivo studies showed that Cosmc deficiency markedly suppressed breast cancer cell growth compared with the corresponding controls. Mechanistically, Cosmc disruption impaired the protein expression of CD44 and the associated MAPK signaling pathway; the latter plays a crucial role in cell proliferation. Reconstitution of CD44 substantially reversed the observed alterations, confirming that CD44 requires normal O-glycosylation for its proper expression and activation of the related signaling pathway.
Conclusion: This study showed that Cosmc deficiency-mediated aberrant O-glycosylation suppressed breast cancer cell growth, which was likely mediated by the impairment of CD44 expression.
Keywords: breast cancer, O-glycosylation, Tn antigen, tumor growth