110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

原花青素化合物(PC)通过阻断 TLR4/NF-κB 信号通路抑制脂多糖诱导的宫颈癌细胞增殖
Authors Yang H, Fang Z, Qu X, Zhang X, Wang Y
Received 8 August 2019
Accepted for publication 20 November 2019
Published 22 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 497—509
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S226547
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
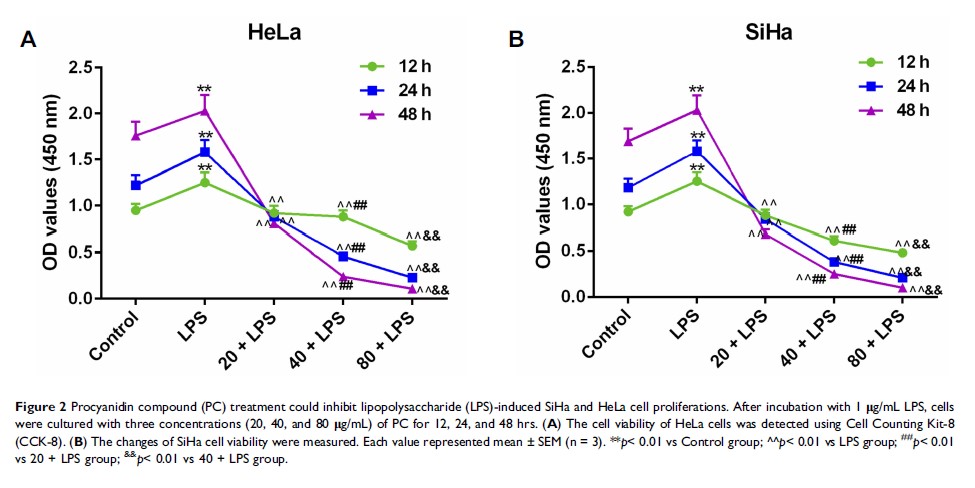
Purpose: Evidence suggested that procyanidin compound (PC) could inhibit the progression of cervical cancer (CC); however, the mechanism still remains unclear. We aimed to study the potential mechanism of PC acting on CC cells.
Patients and Methods: After a 24 hr incubation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1 μg/mL), human CC SiHa and HeLa cells were cultured with various concentrations (20, 40, and 80 μg/mL) of PC for 24 hrs, then the cell viability was detected using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). The migration and invasion abilities were assessed by scratch and Transwell assays. Apoptosis and cell cycle were detected using flow cytometry. Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and Western blot were used for expression analysis of the inflammatory cytokines. The pathway components were measured to evaluate the involvement of toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (TLR4/NF-κB) pathway.
Results: PC inhibited the LPS-primed cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. After PC treatment, cell migration and invasion were inhibited, cell number at the G2/M phase was increased. The CC cell apoptosis was triggered through upregulating levels of cleaved caspase-3 and Bax and downregulating the level of B-cell lymphoma 2 protein. A significant reduction was shown in the levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Furthermore, a remarkable reduction in the ratio of TLR4 and the p-P65/t-P65 and in the progression of P65 translocation into the nucleus was observed.
Conclusion: Our results revealed that the inhibitory effect of PC on CC cell proliferation relies on the induction of apoptosis and inhibition of inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: apoptosis, cell cycle, inflammatory cytokines, P65-NF-κB translocation