110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文已被撤回:Hsa_circ_RNA_0011780 通过靶向 miR-544a 降低 FBXW7,从而抑制非小细胞肺癌的增殖和转移
Authors Liu Y, Yang C, Cao C, Li Q, Jin X, Shi H
Received 26 October 2019
Accepted for publication 19 December 2019
Published 23 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 745—755
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S236162
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
***本文已被撤回***
Purpose: Circular RNA (circRNA) is involved in the development of various cancers. However, whether circRNA can inhibit the tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is still unclear. We aimed to explore the epigenetic function of tumor-suppressive circRNA (hsa_circ_RNA_0011780) and its downstream regulatory factors in NSCLC.
Patients and Methods: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was used to evaluate hsa_circ_11780 expression in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. The impact of high hsa_circ_11780 expression on overall survival in patients with NSCLC was tested using the Log rank test. The association between decreased hsa_circ_11780 expression and clinicopathological features in patients with NSCLC was analyzed using the Chi-squared test. In vitro cell proliferation and apoptosis were assayed using the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and flow cytometry, respectively. Mice xenograft models were used to determine the tumor promoting effects of hsa_circ_11780 on NSCLC in vivo. The underlying regulatory mechanism was predicted by bioinformatics and verified by a dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA transfection, qPCR, and Western blotting. The correlation between miR-544a and hsa_circ_11780 expression was verified using Spearman correlation coefficient.
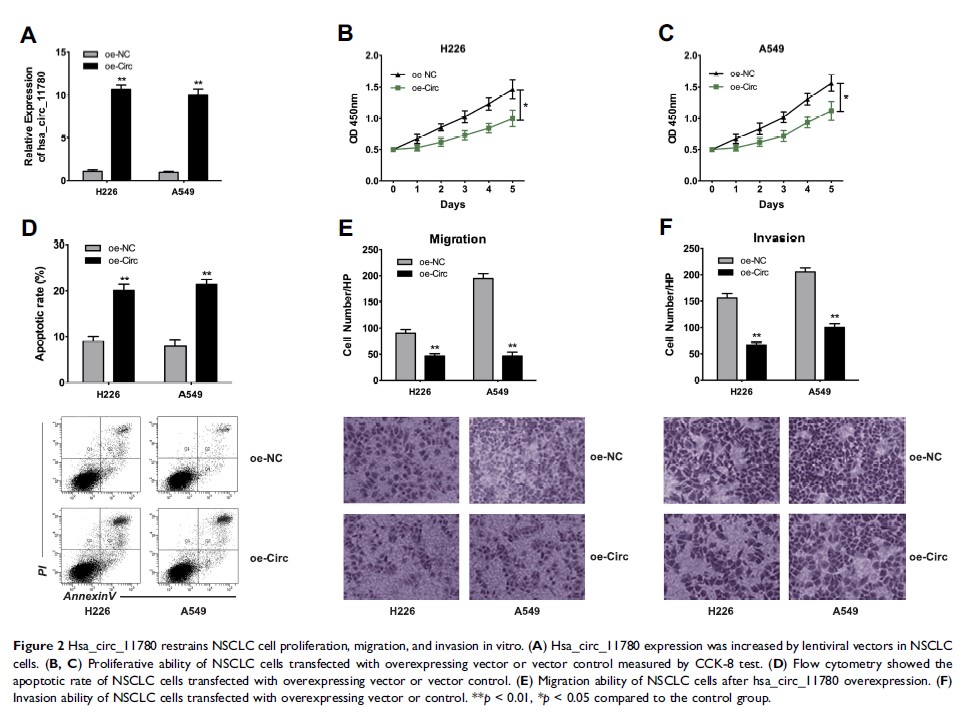
Results: The expression of hsa_circ_11780 in NSCLC tissues and cell lines strongly declined. Low hsa_circ_11780 expression is more likely to present in patients with a large tumor size (> 3cm), distant metastasis, and poor overall survival. hsa_circ_11780 overexpression strongly inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells (H226 and A549) in vitro and inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, hsa_circ_11780 repressed miR-544a function by competitively binding to the complementary sites of miR-544a. miR-544a released by the declining expression of hsa_circ_11780 reduced the protein concentration of F-Box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (FBXW7) in NSCLC cells.
Conclusion: FBXW7 expression mediated by the hsa_circ_11780/miR-544a axis is markedly associated with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC, resulting in decreased survival. These findings suggest that this regulatory axis may serve as a novel therapeutic target in NSCLC.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, hsa_circ_11780, F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7, miR-544a, proliferation, metastasis