110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

布林佐胺/布列莫尼定剂量组合与布林佐胺和溴莫尼定配伍使用在治疗开角型青光眼或眼高压时降低眼压的功效和安全性比较
Authors Wang N, Lu DW, Pan Y, Astakhov Y, Iureva T, Adewale A, Walker TM
Received 17 September 2019
Accepted for publication 31 December 2019
Published 23 January 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 221—230
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S231402
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Objective: To demonstrate that the intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering efficacy of a twice-daily brinzolamide 10 mg/mL (BRINZ)/brimonidine 2 mg/mL (BRIM) fixed-dose combination (BBFC) was non-inferior to its individual components (BRINZ+BRIM) dosed concomitantly in patients with open-angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT). Safety was also evaluated.
Methods and Analysis: This was a Phase III, multicenter, observer-masked study in patients from China, Russia and Taiwan. Patients aged ≥ 18 years with a mean IOP ≥ 21 mmHg and ≤ 36 mmHg in the same eye after washout of other IOP-lowering medications were included. Eligible patients were randomized (1:1) to receive BBFC or BRIZ+BRIM eye drops twice daily for 3 months. The primary endpoint was the mean change in diurnal IOP (averaged over 09:00, +2 h, and +7 h) from baseline to Month 3. Adverse events (AEs) were recorded throughout the study.
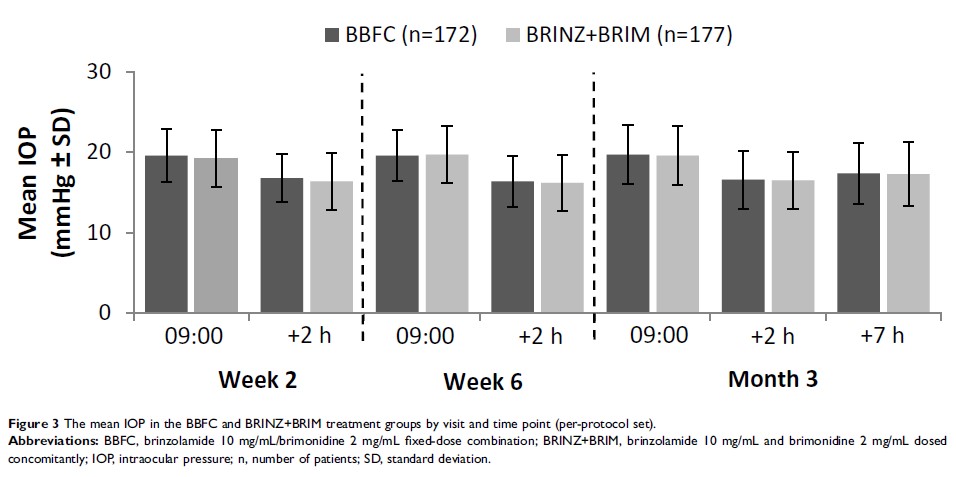
Results: The per-protocol set included 349 patients (BBFC, n=172; BRINZ+BRIM, n=177). The mean±standard deviation diurnal IOP at baseline was 24.6± 2.66 mmHg in both groups. At Month 3, the least square mean±standard error change in diurnal IOP from baseline was − 7.2± 0.34 mmHg and − 7.3± 0.34 mmHg with BBFC and BRINZ+BRIM, respectively (between-group difference: 0.1 mmHg [95% CI − 0.5, 0.7]). In the BBFC and BRINZ+BRIM groups, 53.3% and 55.0% of patients achieved a diurnal IOP < 18 mmHg, and 43.2% and 37.4% of patients, respectively, achieved a mean diurnal IOP reduction > 30% from baseline at Month 3. Ocular AEs were reported in 28.7% (BBFC) and 22.5% (BRINZ+BRIM) of patients; conjunctival hyperemia was the most frequent ocular AE (BBFC, 6.4%; BRINZ+BRIM, 6.8%). Non-ocular AEs were reported in 32.4% (BBFC) and 30.4% (BRINZ+BRIM) of patients.
Conclusion: The study findings demonstrate that the efficacy of twice-daily BBFC was non-inferior to BRINZ+BRIM in patients with OAG/OHT. The safety profile of BBFC was similar to that of BRINZ+BRIM.
Keywords: brinzolamide/brimonidine fixed-dose combination, intraocular pressure reduction, ocular hypertension, open-angle glaucoma