110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在利用介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子-PEI-肽系统进行骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中,miR-26a 所起的作用
Authors Yan J, Lu X, Zhu X, Hu X, Wang L, Qian J, Zhang F, Liu M
Received 27 August 2019
Accepted for publication 28 December 2019
Published 23 January 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 497—511
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S228797
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
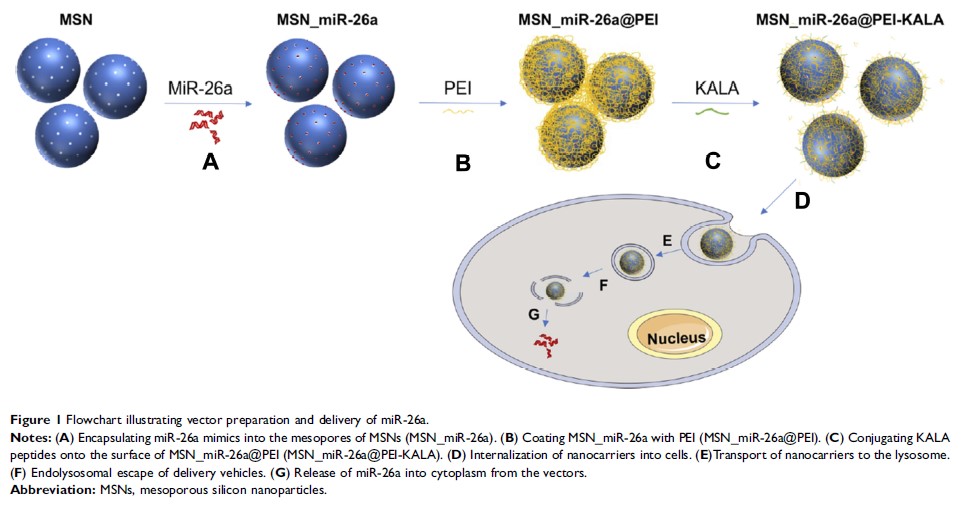
Introduction: RNA-based therapy for bone repair and regeneration is a highly safe and effective approach, which has been extensively investigated in recent years. However, the molecular stability of RNA agents still remains insufficient for clinical application. High porosity, tunable size, and ideal biodegradability and biosafety are a few of the characters of mesoporous silicon nanoparticles (MSNs) that render them a promising biomaterial carrier for RNA treatment.
Materials and Methods: In this study, a novel miR-26a delivery system was constructed based on MSNs. Next, we assessed the miRNA protection of the delivery vehicles. Then, rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (rBMSCs) were incubated with the vectors, and the transfection efficiency, cellular uptake, and effects on cell viability and osteogenic differentiation were evaluated.
Results: The results demonstrated that the vectors protected miR-26a from degradation in vitro and delivered it into the cytoplasm. A relatively low concentration of the delivery systems significantly increased osteogenic differentiation of rBMSCs.
Conclusion: The vectors constructed in our study provide new methods and strategies for the delivery of microRNAs in bone tissue engineering.
Keywords: nanocarrier, microRNAs, osteoinduction, tissue engineering