110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

永久性躯体形式疼痛障碍患者异常的以丘脑为中心的功能连接
Authors Sun X, Pan X, Ni K, Ji C, Wu J, Yan C, Luo Y
Received 18 September 2019
Accepted for publication 11 January 2020
Published 23 January 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 273—281
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S231555
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jun Chen
Purpose: Recent task-based fMRI studies have shown that Persistent Somatoform Pain Disorder (PSPD) patients demonstrated aberrant activity in a wide range of brain regions associated with sensation, cognition and emotion. However, these specific task-based studies could not clearly uncover the alterations in the spontaneous brain networks that were associated with the general pain-related symptoms in PSPD.
Patients and Methods: In the present study, 13 PSPD patients and 23 matched healthy controls (HCs) were enrolled. Resting state and 3D structural imaging data were collected during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Ninety regions of interest (ROIs) were selected from the automated anatomical labeling (AAL) template. The functional connectivity toolbox “CONN” was used to calculate the functional connectivity (FC) coefficients.
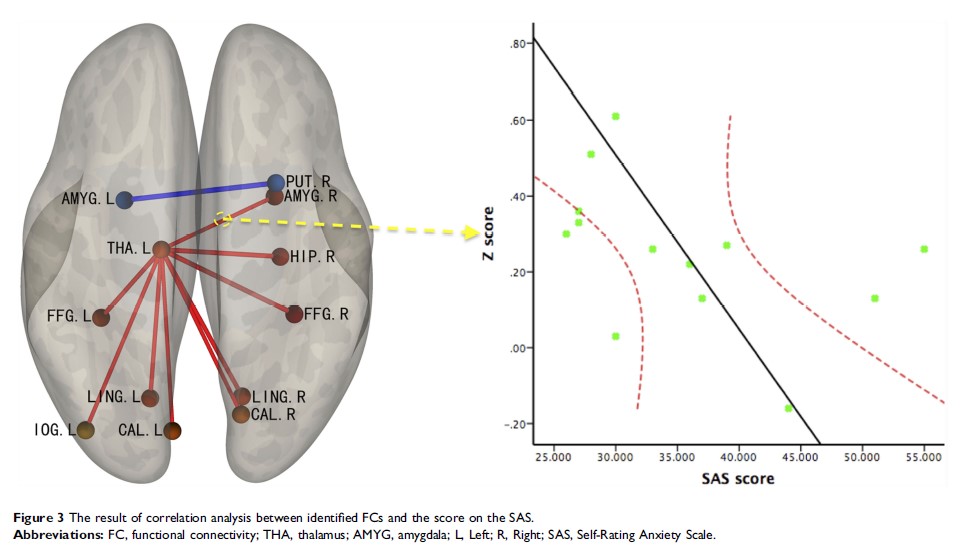
Results: Our results showed that PSPD patients exhibited increased FCs between the left thalamus and the right amygdala, the right hippocampus, and multiple sub-regions of the occipital lobe when compared to HCs. Correlation analysis revealed a negative correlation between the left thalamus-right amygdala FC and the level of anxiety in PSPD patients.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that the altered FC between thalamus and amygdala may be the neural mechanisms underlying the pain-related anxiety in PSPD.
Keywords: persistent somatoform pain disorder, functional magnetic resonance imaging, resting-state, functional connectivity