110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

负载柔红霉素的 CdTe QD 与抗 CD123 单克隆抗体(mAb)结合:用于骨髓增生异常综合征治疗的新型递送系统
Authors Guo D, Xu P, Chen D, Wang L, Zhu Y, Zuo Y, Chen B
Received 4 October 2019
Accepted for publication 9 January 2020
Published 24 January 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 521—536
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S233395
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Introduction: The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a very heterogeneous group of myeloid disorders characterized by peripheral blood cytopenias and increase risk of transformation to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Daunorubicin (DNR) is an indispensable drug for the treatment of MDS and AML. However, its side effects including cardiac toxicity and bone marrow suppression severely limit clinical application. Many researches reported high expression of CD123 antigen on high-risk MDS cells, so we constructed a novel drug delivery system comprising daunorubicin-loaded CdTe QDs conjugated with anti-CD123 mAbs (DNR-CdTe-CD123) to develop targeted combination chemotherapy for MDS.
Methods: CdTe conjugated antiCD123 through amide bond, co-loaded with DNR with electrostatic bonding. Then, we determined characterization and release rate of DNR-CdTe-CD123. The therapeutic effect and side effect of drug delivery system were evaluated through in vitro and in vivo experiments.
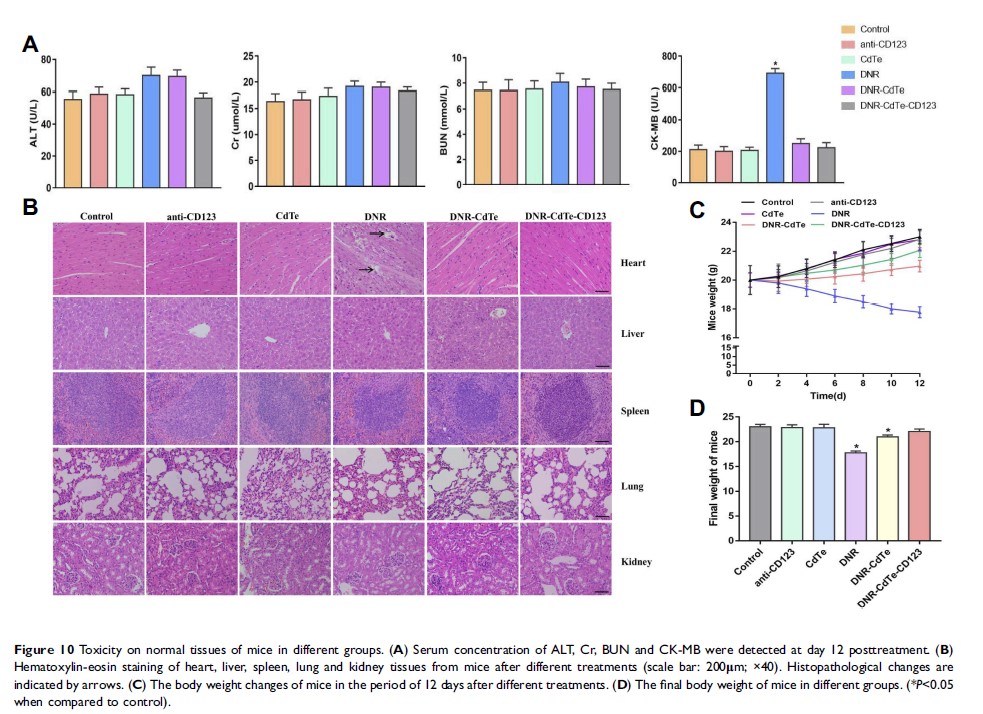
Results: CdTe showed appropriate diameter and good dispersibility and DNR was loaded into CdTes with high encapsulation efficiency and drug loading. The maximum drug loading and encapsulation efficiency were 42.08 ± 0.64% and 74.52 ± 1.81%, respectively, at DNR concentration of 0.2mg/mL and anti-CD123 mAbs volume of 5ul (100ug/mL). Flow cytometry (FCM) showed that CD123 antigen was highly expressed on MUTZ-1 cells, and its expression rate was 72.89 ± 10.67%. In vitro experiments showed that the inhibition rate and apoptosis rate of MUTZ-1 cells treated with DNR-CdTe-CD123 were higher than those in the other groups (P < 0.05). Compared with the other groups, the level of apoptosis-related protein (P53, cleaved caspase-9, Bax and cleaved caspase-3) were upregulated in DNR-CdTe-CD123 group (P < 0.05). In vivo experiments, DNR-CdTe-CD123 can effectively inhibit the tumor growth of MDS-bearing nude mice and reduce the side effects of DNR on myocardial cells.
Conclusion: The system of DNR-CdTe-CD123 enhances the therapeutic effects and reduce the side effects of DNR, thus providing a novel platform for MDS treatment.
Keywords: myelodysplastic syndrome, daunorubicin, CdTe, anti-CD123 monoclonal antibody, drug delivery system