110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

核仁和纺锤体相关蛋白 1(NUSAP1)通过 TGF-β 信号通路促进膀胱癌进展
Authors Gao S, Yin H, Tong H, Zhan K, Yang G, Hossain MA, Li T, Gou X, He W
Received 3 November 2019
Accepted for publication 10 January 2020
Published 28 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 813—825
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S237127
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Purpose: NUSAP1 has been reported to be involved in the progression of several types of cancer. However, its expression and exact role in bladder cancer (BLCA) remains elusive. The aim of this study was to determine the expression and role of NUSAP1 in BLCA.
Methods: Tissue microarray, real-time PCR, Western blot and immunohistochemistry assays were carried out to determine NUSAP1 expression in BLCA tissues and cells. The biological roles of NUSAP1 were investigated using CCK-8, EdU labeling, flow cytometry, Transwell, and wound healing assays. Additionally, the effect of NUSAP1 on epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) was investigated by Western blotting and real-time PCR.
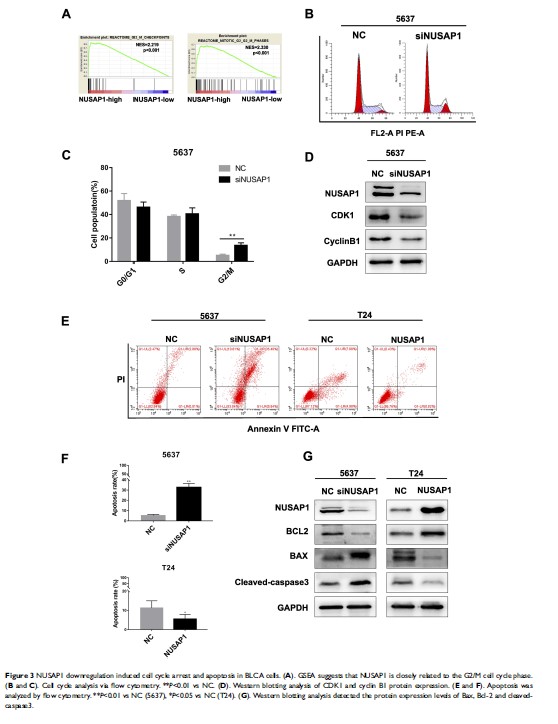
Results: We found that NUSAP1 was upregulated in BLCA, and its expression was closely related to the poor prognosis of patients. Subsequently, we transfected 5637 and T24 cell lines with NUSAP1 siRNA and an NUSAP1 overexpression plasmid, respectively. NUSAP1 downregulation in 5637 cells inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasiveness and enhanced chemosensitivity to gemcitabine, while NUSAP1 overexpression in T24 cells resulted in the inverse effects. Moreover, NUSAP1 regulated EMT via the TGF-β signaling pathway, and when TGF-beta receptor 1 (TGFBR1) was inhibited with the inhibitor SB525334, the invasion and metastasis ability of BLCA cells was significantly suppressed, as well as p-Smad2/3 and vimentin expression.
Conclusion:
Keywords: NUSAP1, bladder cancer, tumor progression, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, TGF-β signaling pathway