110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

减少微管微丝交联因子 1 通过减少上皮间质转化来抑制黑素瘤转移
Authors Wang X, Jian X, Dou J, Wei Z, Zhao F
Received 29 August 2019
Accepted for publication 28 December 2019
Published 29 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 663—673
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S229156
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yong Teng
Background: The microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1 (MACF1) is involved in cellular migration, adhesion, and invasion processes. Its abnormal expression initiates tumor cell proliferation and metastasis in numerous cancer types.
Methods: In this study, we utilized short hair-pin RNA interference of MACF1 to assess the inhibitory effects on the metastatic potential of B16F10 melanoma cells both in vitro and in vivo a mouse model.
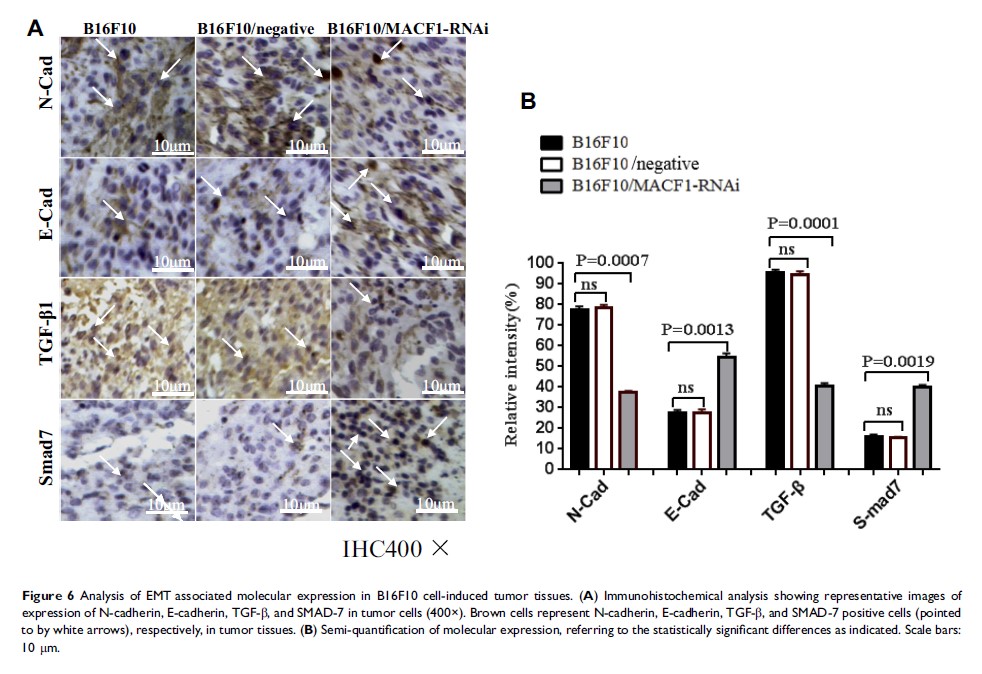
Results: The MACF1 expression was increased in B16F10 cells-induced tumor tissues; while the down-regulation of MACF1 impacted the B16F10 melanoma cell metastatic behavior by decreasing the ability of colony formation and invasion in vitro as well as inhibiting B16F10 cells-induced tumor growth and lung metastasis in vivo. The results of Western blot and immunohistochemistry indicated that the expression of E-cadherin and Smad-7 was significantly increased whereas the expression of N-cadherin and TGF-β 1 was significantly decreased in tumor tissue of mice challenged with the B16F10/MACF1-RNAi cells when compared with the B16F10 cells challenged mice.
Conclusion: The data presented in this study demonstrated that down-regulated MACF1 expression decreased B16F10 melanoma metastasis in mice by inhibiting the epithelial to mesenchymal transition program. Thus, MACF1 may be a novel target for melanoma therapy.
Keywords: melanoma, microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1, metastasis, epithelial to mesenchymal transition