110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

黄 ical 苷通过 AMPK-mTOR 信号通路诱导自噬,可以保护人类皮肤成纤维细胞免受由紫外线 B 辐射而诱导的细胞凋亡
Authors Zhang JA, Luan C, Huang D, Ju M, Chen K, Gu H
Received 22 August 2019
Accepted for publication 10 January 2020
Published 29 January 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 417—428
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S228047
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Background: Baicalin, a natural product isolated from Scutellaria radix, has been reported to exert anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic effects on skin, but the underlying mechanism remains poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate the possible mechanism of anti-UVB effect of baicalin in human skin fibroblasts.
Methods: Cell proliferation was estimated by CCK-8 Kit. Apoptotic incidence was detected by flow cytometry with Annexin V-PE/PI apoptosis detection kit. Autophagy was determined by the evaluation of fluorescent LC3 puncta and Western blotting. Cell signalling was analysed by Western blotting.
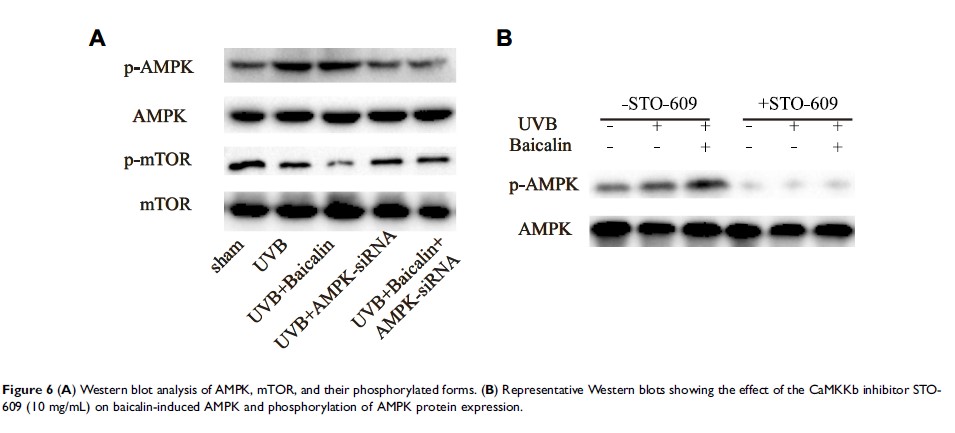
Results: Baicalin exerted cytoprotective effects in UVB-induced HSFs. Moreover, baicalin increased autophagy and suppressed UVB-induced apoptosis of HSFs. Pretreatment with 3-MA, an autophagy inhibitor, attenuated baicalin-induced HSFs autophagy and promoted apoptosis. Baicalin activated AMPK, which leads to suppression of basal mTOR activity in cultured HSFs. Administration of compound C, an AMPK inhibitor, abrogated AMPK phosphorylation and increased mTOR phosphorylation and apoptosis compared with baicalin alone.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results indicate the important role of mTOR inhibition in UVB protection by baicalin and provide a new target and strategy for better prevention of UV-induced skin disorders.
Keywords: autophagy, baicalin, ultraviolet B, apoptosis, AMPK