110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小檗碱的抗癌机制:综述
Authors Wang Y, Liu Y, Du X, Ma H, Yao J
Received 13 December 2019
Accepted for publication 22 January 2020
Published 30 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 695—702
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S242329
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
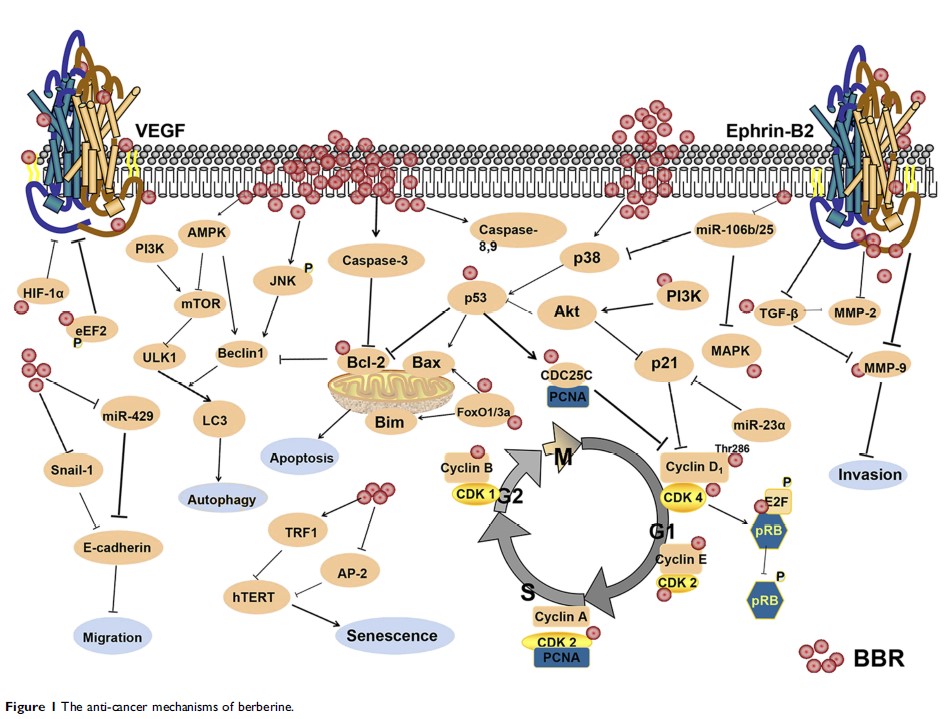
Abstract: Berberine (BBR) has been extensively studied in vivo and vitro experiments. BBR inhibits cell proliferation by regulating cell cycle and cell autophagy, and promoting cell apoptosis. BBR also inhibits cell invasion and metastasis by suppressing EMT and down-regulating the expression of metastasis-related proteins and signaling pathways. In addition, BBR inhibits cell proliferation by interacting with microRNAs and suppressing telomerase activity. BBR exerts its anti-inflammation and antioxidant properties, and also regulates tumor microenvironment. This review emphasized that BBR as a potential anti-inflammation and antioxidant agent, also as an effective immunomodulator, is expected to be widely used in clinic for cancer therapy.
Keywords: berberine, anti-tumor, traditional Chinese medicine, cancer