110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

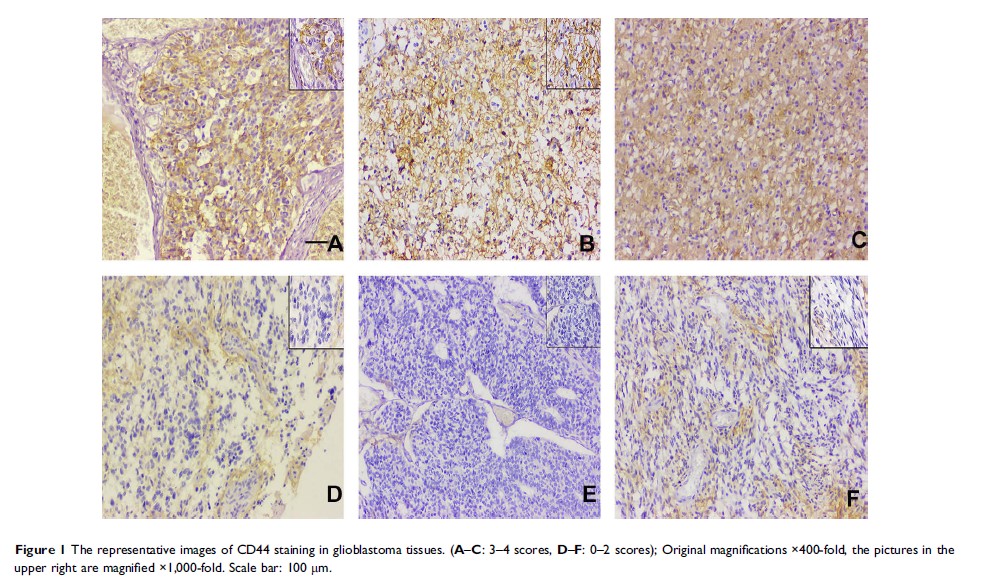
CD44 的高表达预测胶质母细胞瘤的预后不良
Authors Si D, Yin F, Peng J, Zhang G
Received 4 October 2019
Accepted for publication 15 January 2020
Published 3 February 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 769—775
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S233423
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common of the malignant and invasive gliomas. High grade glioma is prone to relapse and has a poor prognosis. However, there is a big difference in terms of survival time with the same grade glioma. Cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) is an indicator of cancer stem cells with abnormal expression in many malignant tumors, however the expression in GBM is unknown.
Methods: Tissue specimens were collected from 62 GBM patients to investigate CD44 expression and their prognosis was followed-up. Chi-square test was used to identify the association between CD44 staining and clinical characteristics of the patients. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to draw survival curves and Cox regression analysis to confirm the independent prognostic factors of GBM patients.
Results: In total, 38.7% (24/62) of the patients had high CD44 staining. The median survival times were 3.5 months and 18.5 months for high and low expressions of CD44, respectively. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that tumor location, the extent of tumor resection, adjuvant chemotherapy, and CD44 expression were related to overall survival time of GBM patients (P <0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that non-usage of adjuvant chemotherapy (HR=4.097, 95% CI=1.489– 11.277, P =0.006) and CD44 overexpression (HR=3.216, 95% CI=1.452– 7.125, P =0.004) were independent unfavorable prognostic factors for GBM patients.
Conclusion: The results demonstrate that high expression of CD44 acts as a poor prognosis indicator in GBM patients.
Keywords: glioblastoma, CD44, immunohistochemistry, survival times