110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二甲双胍通过调节 lncRNA TUG1 诱导自噬并抑制动脉粥样硬化来激活 AMPK-mTOR 信号通路
Authors You G, Long X, Song F, Huang J, Tian M, Xiao Y, Deng S, Wu Q
Received 10 October 2019
Accepted for publication 11 January 2020
Published 3 February 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 457—468
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S233932
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios D. Panos
Background: Metformin has been shown to inhibit the proliferation and migration of vascular wall cells. However, the mechanism through which metformin acts on atherosclerosis (AS) via the long non-coding RNA taurine up-regulated gene 1 (lncRNA TUG1 ) is still unknown. Thus, this research investigated the effect of metformin and lncRNA TUG1 on AS.
Methods: First, qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of lncRNA TUG1 in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD). Then, the correlation between metformin and TUG1 expression in vitro and their effects on proliferation, migration, and autophagy in vascular wall cells were examined. Furthermore, in vivo experiments were performed to verify the anti-AS effect of metformin and TUG1 to provide a new strategy for the prevention and treatment of AS.
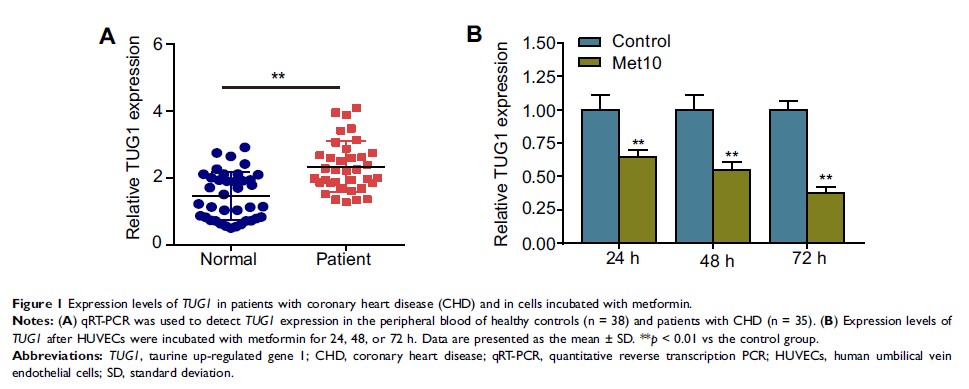
Results: qRT-PCR results suggested that lncRNA TUG1 expression was robustly upregulated in patients with CHD. In vitro experiments indicated that after metformin administration, the expression of lncRNA TUG1 decreased in a time-dependent manner. Metformin and TUG1 knockdown via small interfering RNA both inhibited proliferation and migration while promoted autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR pathway in vascular wall cells. In vivo experiments with a rat AS model further demonstrated that metformin and sh-TUG1 could inhibit the progression of AS.
Conclusion: Taken together, our data demonstrate that metformin might function to prevent AS by activating the AMPK/mTOR pathway via lncRNA TUG1 .
Keywords: metformin, taurine up-regulated gene 1, AMPK/mTOR, autophagy, atherosclerosis