110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

组蛋白甲基转移酶 SETDB2 在 AML1-ETO 阳性的急性髓系白血病(AML)中的致癌作用
Authors Mu G, Chen F
Received 13 August 2019
Accepted for publication 4 November 2019
Published 4 February 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 783—792
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S227036
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
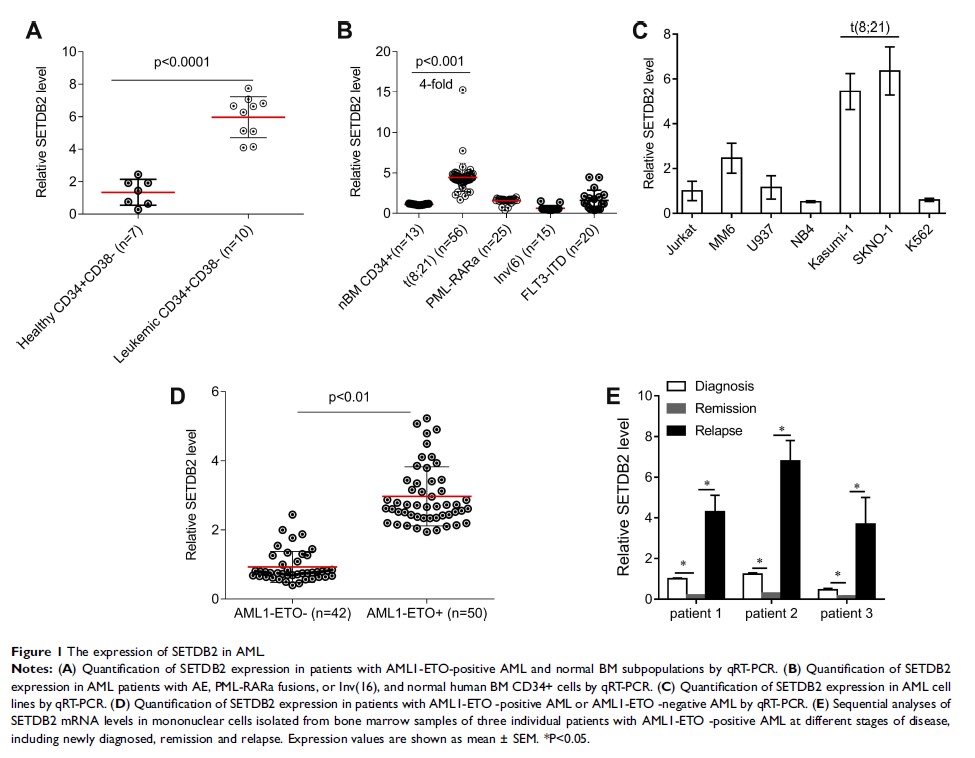
Introduction: AML1-ETO produced by t(8;21) abnomality has multiple effects on the leukemogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). SET domain, bifurcated 2 (SETDB2) can mediate gene silencing by trimethylation of the ninth lysine residue of histone H3 protein (H3K9) of the promoter and has been confirmed as an oncogene in many cancers. The role of SETDB2 in AML1-ETO positive AML is not clear.
Methods: Quantitative reverse transcription PCR was performed to measure SETDB2 expression in bone marrow from AML patients and healthy people. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to investigate the effect of SETDB2 on prognosis of AML patients. Dual luciferase reporter gene assay, chromatin immunoprecipitation were performed to investigate the regulatory mechanism of AML1-ETO on SETDB2. CCK-8 and colony formation assay were performed to measure the effect of SETDB2 on leukemic cells.
Results: SETDB2 is highly expressed in AML1-ETO positive AML. The overall survival, event-free and relapse-free survival rate of patients with high SETDB2 expression was lower than those of patients with low SETDB2 expression. SETDB2 is epigenetically upregulated by AML1-ETO fusion protein. Downregulation of SETDB2 expression significantly inhibits the proliferation and clonality of leukemic cells and promotes the sensitivity of leukemic cells to an epigenetic inhibitor JQ1.
Conclusion: AML1-ETO/SETDB2 is a novel epigenetic pathway of leukemogenesis and SETDB2 is a potential therapeutic target of t(8;21) AML.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia, AML1-ETO, SETDB2, epigenetic, clinical biomarker