110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

腰围与小腿围的比率是百岁老人 HRQoL 的独立危险因素
Authors Yang S, Liu M, Wang S, Jia W, Han K, He Y
Received 17 September 2019
Accepted for publication 15 January 2020
Published 4 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 277—287
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S231435
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Juei-Tang Cheng
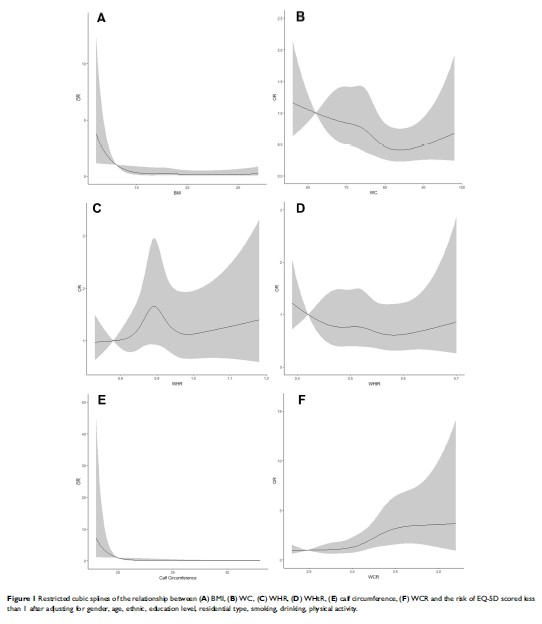
Purpose: To analyze the associations between waist circumference (WC), body mass index (BMI), waist–hip ratio (WHR), waist–height ratio (WHtR), calf circumference, waist-calf circumference ratio (WCR), and quality of life in Hainan centenarians.
Patients and Methods: A total of 1002 centenarians in Hainan were selected by a full sample survey. The EQ-5D visual analogue scale (EQ-5D-VAS) was used to investigate the quality of life. Restricted cubic splines were used to analyze and visualize the linear relationships.
Results: After adjustment, the standard β values for BMI, WC, WHR, WHtR, calf circumference, and WCR associated with EQ-5D score were 0.101, 0.126, − 0.018, 0.100, 0.302, and − 0.219, respectively; all associations except for WHR were significant (P < 0.01). With increasing BMI, WC, and calf circumference, the risk of EQ-5D score < 1 decreased (odds ratios [ORs] 0.91 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.86– 0.97), 0.97 [95% CI: 0.95– 0.99], and 0.87 [95% CI: 0.82– 0.92] after adjustment, respectively). With increasing WCR, the risk also increased (OR 2.70 [95% CI: 1.54– 4.75]).
Conclusion: After excluding nutritional and muscle retention factors, fat central distribution negatively impacted the health-related quality of life of the oldest old population.
Keywords: centenarians, waist–calf circumference ratio, quality of life, obesity