110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA HULC 通过 miR-218/TPD52 轴促进宫颈癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Lu W, Wan X, Tao L, Wan J
Received 29 September 2019
Accepted for publication 12 December 2019
Published 5 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1109—1118
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S232914
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Objective: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been identified as important players in tumorigenesis. LncRNA highly upregulated in liver cancer (HULC) has been identified as a key regulator in the progression of various cancers. However, the functional role and the mechanisms of HULC in regulating cervical cancer cell behavior remain unclear.
Methods: HULC expression, miR-218 expression and TPD52 mRNA level in cervical cancer cells were examined by qRT-PCR. Cell proliferation was evaluated by MTT assay. Cell migration and invasion were examined by Transwell assay. TPD52 protein level was measured by Western blot. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was measured to verify the combination of HULC and miR-218 as well as miR-218 and TPD52.
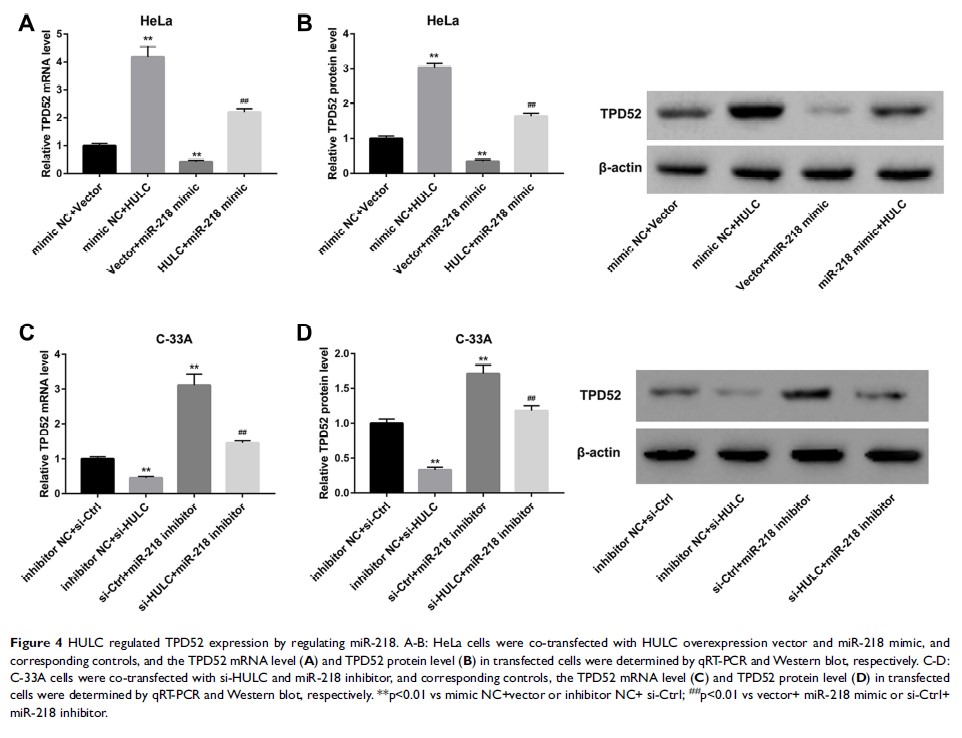
Results: HULC expression was upregulated in cervical cancer cell lines, and HULC promoted cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Mechanistically, HULC acted as a sponge of miR-218 to elevate expression of TPD52, a target of miR-218, and thereby promoted cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Conclusion: HULC promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via miR-218/TPD52 axis.
Keywords: HULC, miR-218, TPD52, cervical cancer cell proliferation