110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由 NAG 引导的纳米递送系统,用于癌细胞中由氧化还原和 pH 触发的细胞内药物按顺序释放
Authors Liang Y, Zhang J, Tian B, Wu Z, Svirskis D, Han J
Received 6 August 2019
Accepted for publication 10 December 2019
Published 5 February 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 841—855
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S226249
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Aim: Sequential treatment with paclitaxel (PTXL) and gemcitabine (GEM) is considered clinically beneficial for non-small-cell lung cancer. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of a nano-system capable of sequential release of PTXL and GEM within cancer cells.
Methods: PTXL-ss-poly(6-O -methacryloyl-d-galactopyranose)-GEM (PTXL-ss-PMAGP-GEM) was designed by conjugating PMAGP with PTXL via disulfide bonds (-ss-), while GEM via succinic anhydride (PTXL:GEM=1:3). An amphiphilic block copolymer N-acetyl-d-glucosamine(NAG)-poly(styrene-alt-maleic anhydride)58-b-polystyrene130 acted as a targeting moiety and emulsifier in formation of nanostructures (NLCs).
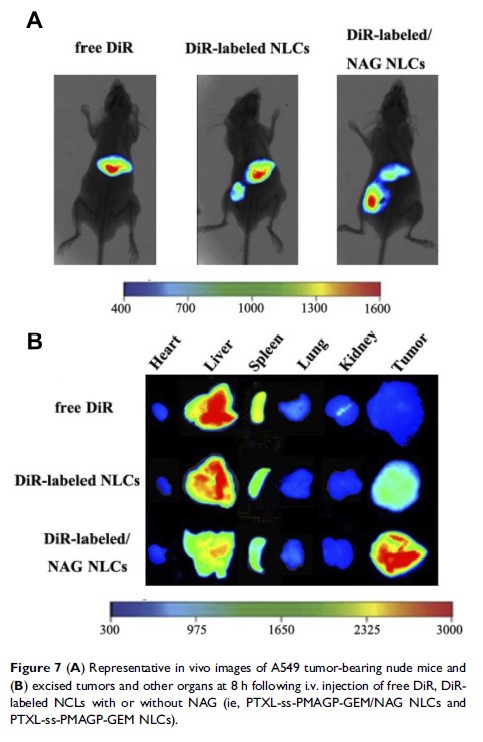
Results: The PTXL-ss-PMAGP-GEM/NAG NLCs (119.6 nm) provided a sequential in vitro release of, first PTXL (redox-triggered), then GEM (pH-triggered). The redox- and pH-sensitive NLCs readily distributed homogenously in the cytoplasm. NAG augmented the uptake of NLCs by the cancer cells and tumor accumulation. PTXL-ss-PMAGP-GEM/NAG NLCs exhibited synergistic cytotoxicity in vitro and strongest antitumor effects in tumor-bearing mice compared to NLCs lacking pH/redox sensitivities or free drug combination.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated the abilities of PTXL-ss-PMAGP-GEM/NAG NLCs to achieve synergistic antitumor effect by targeted intracellularly sequential drug release.
Keywords: sequential release, redox-sensitive, pH-sensitive, synergistic efficiency, combination drug delivery, gemcitabine, paclitaxel