110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Caspase-3 通过由 Gasdermin E 介导的细胞凋亡过程中的继发性坏死,促进糖尿病性肾脏疾病的恶化
Authors Wen S, Wang ZH, Zhang CX, Yang Y, Fan QL
Received 12 December 2019
Accepted for publication 16 January 2020
Published 10 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 313—323
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S242136
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
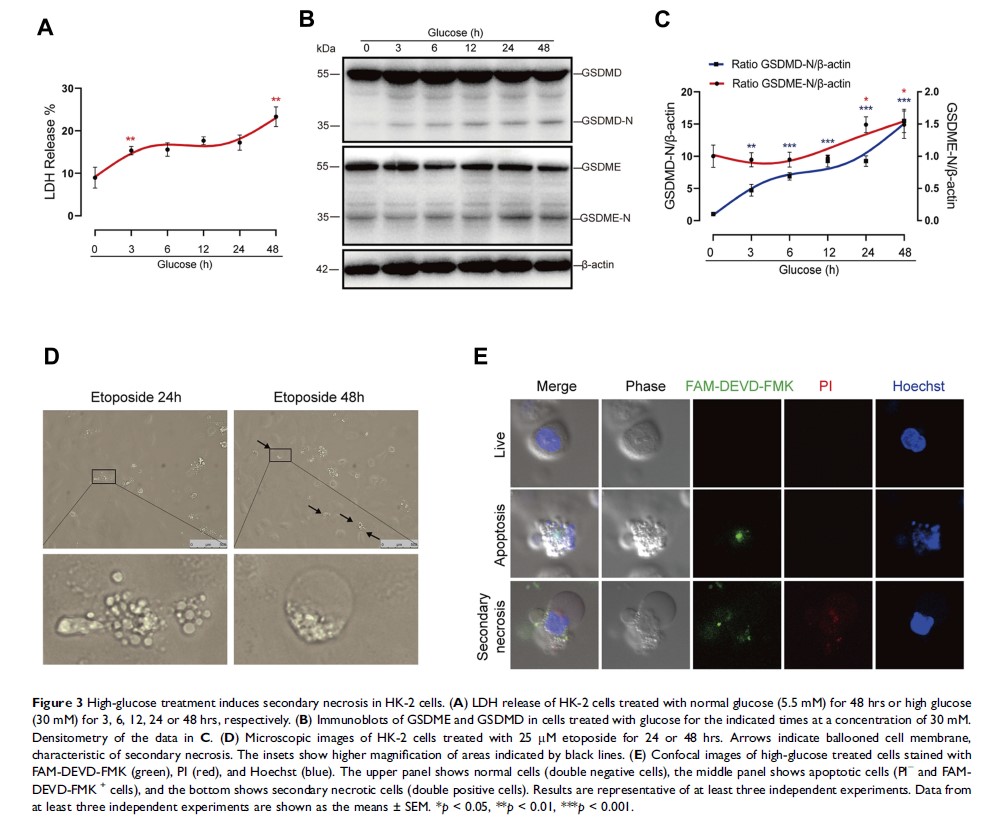
Background: Apoptosis has been repeatedly linked with diabetic kidney disease (DKD), which is a programmed cell death mediated by effector caspases-3, 6 and 7, targeting > 600 substrates. However, the pathophysiologic correlations of this process remain obscure. As a putative tumor suppressor, gasdermin E (GSDME) was recently reported to be cleaved by caspase-3 to produce a GSDME-N fragment which targets the plasma membrane to switch apoptosis to secondary necrosis. However, it remains elusive whether GSDME is involved in the regulation of DKD.
Methods: To evaluate the therapeutic potential of caspase-3 inhibition in DKD, we administered caspase-3 inhibitor Z-DEVD-FMK to STZ-induced diabetic mice for eight weeks. Albuminuria, renal function, pathological changes, and indicators of secondary necrosis and fibrosis were evaluated. In vitro, human tubule epithelial cells (HK-2 cells) were subjected to high-glucose treatment. Secondary necrosis was determined by LDH release, GSDME cleavage, and morphological feature under confocal microscopy. Z-DEVD-FMK and GSDME inhibition by shRNA were administered to suppress the cleavage and expression of GSDME. Flow cytometry, cytotoxicity assay and immunoblot were used to assess cell death and fibrogenesis.
Results: Caspase-3 inhibition by Z-DEVD-FMK ameliorated albuminuria, renal function, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in diabetic mice. The nephroprotection mediated by Z-DEVD-FMK was potentially associated with inhibition of GSDME. In vitro, molecular and morphological features of secondary necrosis were observed in glucose-stressed HK-2 cells, evidenced by active GSDME cleavage, ballooning of the cell membrane, and release of cellular contents. Here we showed that caspase-3 inhibition prevented GSDME activation and cell death in glucose-treated tubular cells. Specifically, knocking down GSDME directly inhibited secondary necrosis and fibrogenesis.
Conclusion: These data suggest GSDME-dependent secondary necrosis plays a crucial role in renal injury, and provides a new insight into the pathogenesis of DKD and a promising target for its treatment.
Keywords: GSDME, DFNA5, secondary necrosis, diabetic kidney disease, Z-DEVD-FMK