110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

《续药和服药依从性量表(ARMS)》(中文版)的心理计量评估与老年高血压患者的血压控制
Authors Chen YJ, Chang J, Yang SY
Received 27 October 2019
Accepted for publication 25 December 2019
Published 10 February 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 213—220
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S236268
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Objective: This study aimed to develop the ARMS-C and test its psychometric properties in hypertensive patients, to assess the level of medication adherence and to identify associated predictors for medication adherence and blood-pressure control among Chinese hypertensive patients.
Methods: Hypertensive elderly who met inclusion criteria were recruited from an aged-care facility in Henan Province between January 2019 and July 2019. The patients completed the adapted ARMS-C. The scale’s factor structure, internal consistency, and construct validity were tested.
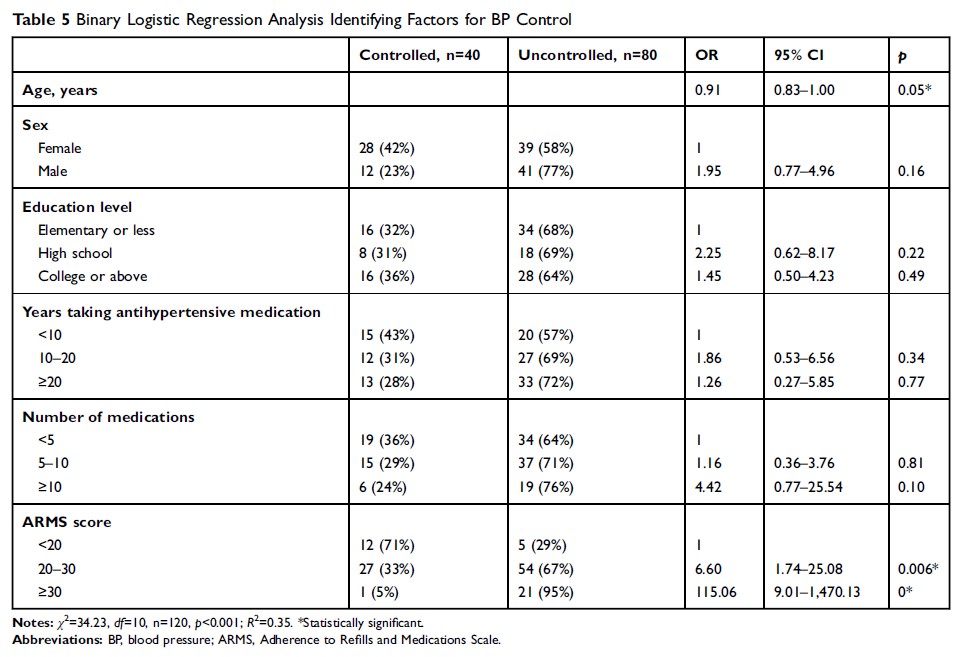
Results: Good internal consistency (Cronbach’s α =0.89) and test–retest reliability (r =0.86, p < 0.01) were obtained. Item-total correlation coefficients for the ten-item ARMS-C were 0.505– 0.801. Factor analysis of construct validity identified two factors, explaining a total variance of 63.3%. Binary regression showed that patients with scores at level 2 (≤ 20 ARMS-10 scores < 30) were six times as likely to have blood pressure uncontrolled as those at level 1 (ARMS-10 scores < 20, OR 6.6, 95% CI 1.7– 25.1; p =0.006), and patients with scores at level 3 (ARMS-10 scores > 30) were 115 times as likely to have blood pressure uncontrolled as those at level 1 (ARMS-10 scores < 20,OR 115, 95% CI 9– 1,470; p =0).
Conclusion: The ten-item ARMS-C is a reliable and valid self-reporting screening tool for adherence to medication and refills in elderly hypertensive Chinese patients.
Keywords: adherence, 10-item ARMS, hypertension, blood-pressure control