110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

卡博替尼对 CD74-ROS1 融合晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的有效治疗:一份病例报告
Authors Wang G, Gao J, Lv J, Chen X, Wu J, Wang R, Jiang J
Received 15 October 2019
Accepted for publication 17 December 2019
Published 11 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1171—1177
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234733
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
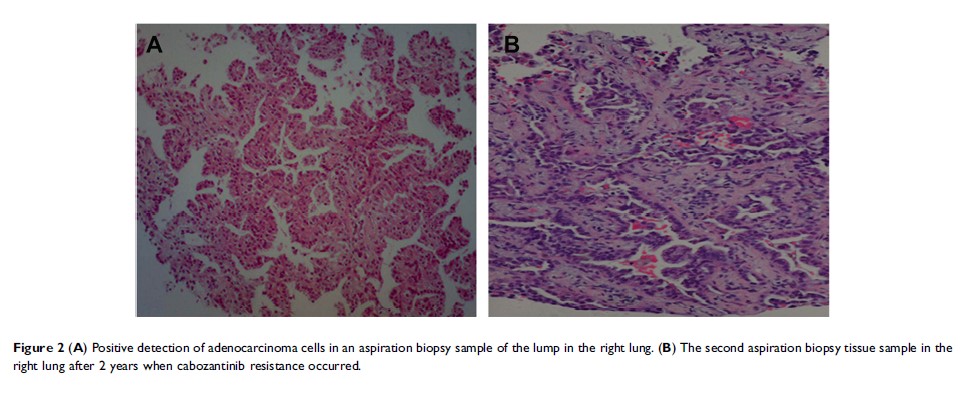
Abstract: Cabozantinib has been shown to have potent anti-ROS1 activity in many solid malignancies, particularly against those with solvent-front resistance mutations following crizotinib therapy. With regard to the most common CD74-ROS1 fusion, the efficacy of cabozantinib has only been demonstrated in vitro. Therefore, we evaluate the efficacy of cabozantinib in a patient with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring a CD74-ROS1 fusion in the present study. A 40-year-old female patient presented with 1-month history of cough, white sputum and chest pain. Chest CT scan revealed a consolidation in the middle lobe of the right lung together with multiple cavity lesions spreading in both lungs. Histopathological analysis of biopsy samples from the lesion in the middle lobe of the right lung suggested lung adenocarcinoma. After two lines of chemotherapy and EGFR-TKI therapy, a CD74-ROS1 rearrangement was detected and the patient was administered with cabozantinib for 1.5 years. Since cabozantinib resistance developed, crizotinib therapy was applied and demonstrated clinical effectiveness until now. Together, we report the first case of cabozantinib effectiveness in treating a CD74-ROS1 -positive advanced NSCLC patient. Crizotinib remained as an effective therapeutic option following the acquisition of cabozantinib resistance.
Keywords: cabozantinib, CD74-ROS1 fusion, NSCLC, crizotinib