110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Id-4 在食管鳞状细胞癌中的表达及其预后价值
Authors Wang X, Lu Q, Fei X, Zhao Y, Shi B, Li C, Chen H
Received 11 September 2019
Accepted for publication 12 December 2019
Published 12 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1225—1234
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S230678
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Background: Our previous study demonstrated that Id-1 may promote the tumorigenicity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Id-4 is another member of Id family, which is rare to be studied in ESCC. In this study, we investigated the expression of Id-4 in human ESCC specimens and determined whether Id-4 expression was associated with the clinicopathologic characteristic and the prognosis of ESCC patients.
Methods: We examined Id-4 expression using immunohistochemistry in 92 ESCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. The association between Id-4 expression and clinical parameters and survival was evaluated by statistical analysis. Cox regression analyses were conducted to identify prognostic factors associated with overall survival (OS). In addition, we explored the functional mechanism of Id-4 in ESCC.
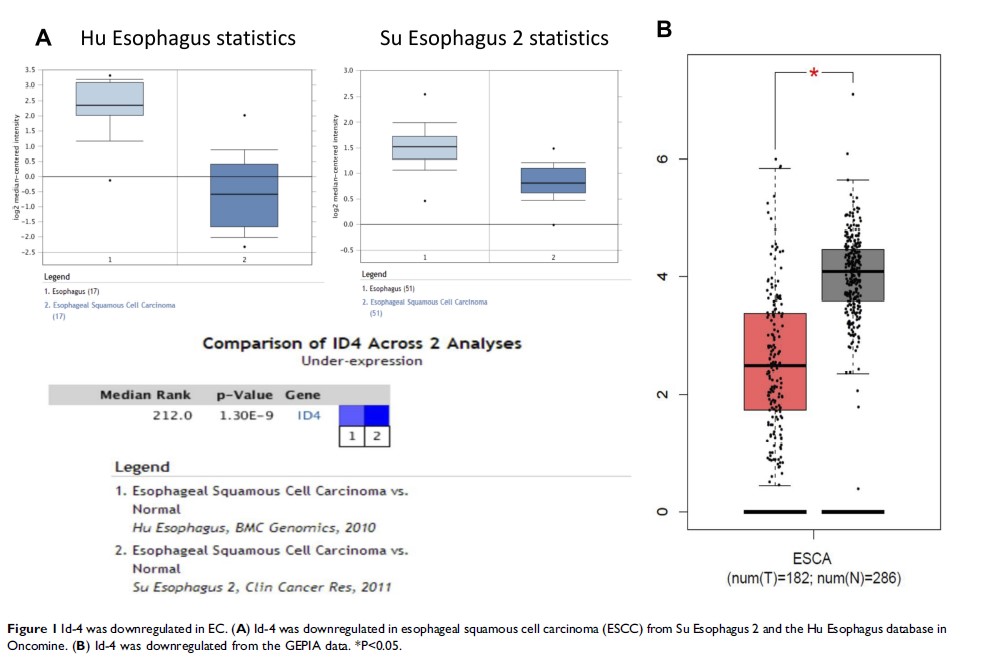
Results: Id-4 expression was significantly downregulated in ESCC tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. The expression of Id-4 was associated negatively with pT stage (p=0.002), AJCC stage (p=0.008) and histologic differentiation (p< 0.001). OS was more unfavorable in patients with low expression of Id-4 than those with high expression of ESCC patients (p=0.007). In subgroup analysis, low expression of Id-4 could reveal unfavorable OS of patients with pT1b/T2 stage (p=0.024) or with pN0/N1 stage (p=0.004). By univariate analysis, pT stage and Id-4 expression showed statistically significant associations with OS (p=0.025, p=0.01, respectively). By multivariate analysis, Id-4 expression was an independent prognostic factor in ESCC (p =0.038). In addition, we observed that Id-4 could decrease the levels of the p-Smad2, p-Smad3 and TGF-β 1 in both Eca109 and TE1 cells, indicating Id-4 may inactivate the TGF-β signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Low expression of Id-4 suggested unfavorable prognosis for ESCC patients and could identify the prognosis in patients of early-stage tumors. The potential mechanism for Id-4’s tumor suppressor role in ESCC may be related to its inhibitory effect on TGF-β signaling pathway. Thus, we believe that Id-4 may be a promising prognostic marker and a therapeutic target in ESCC.
Keywords: Id-4, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, prognosis, TGF-β signaling pathway