111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA X-非活性特异性转录物通过 miR-139-5p/ROCK1 信号通路促进黑色素瘤的细胞功能
Authors Tian K, Sun D, Chen M, Yang Y, Wang F, Guo T, Shi Z
Received 1 August 2019
Accepted for publication 10 December 2019
Published 12 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1277—1287
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S225661
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
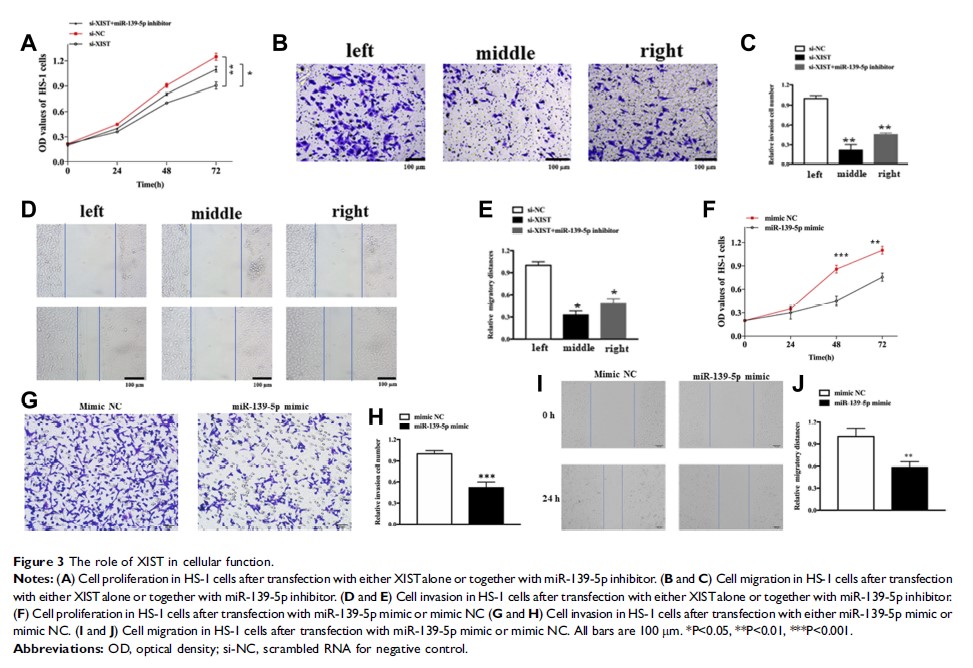
Purpose: Although X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) is known to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of melanoma, the mechanisms through which this remains unclear.
Methods: RNAseq, immunohistochemistry, and qRT-PCR were used to identify the levels of XIST, miR-139-5p, and Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Protein Kinase-1 (ROCK1) in melanoma tissues and cells. A subcellular fractionation assay was used to determine the location of XIST. CCK-8 and colony formation assays were used to evaluate cellular proliferation. Cell migration and wound healing assays were used to detect the effects on cell migration. RNA pull-down was used to confirm the interaction between XIST and miR-139-5p. Besides, the xenograft tumor experiment was performed to further verify the roles of XIST in melanoma.
Results: In this study, an increased level of XIST was revealed in melanoma tissues and cells, which was associated with higher TNM stage and positive lymph node metastasis. XIST was found to function as a “molecular sponge” of miR-139-5p to facilitate cellular functions. Moreover, these consequences could be partially reversed by inhibition of miR-139-5p. MiR-139-5p was found to target ROCK1 directly, leading to suppression of ROCK1 expression; this effect could be partially reversed by inhibiting XIST expression. Furthermore, the deletion of ROCK1 induced anti-oncogenic effects similar to those seen with knockout of XIST. Upregulation of miR-139-5p and knockdown of XIST could inhibit cell functions in melanoma.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that the lncRNA XIST facilitates cellular functions in melanoma via the miR-139-5p/ROCK1 pathway.
Keywords: LncRNA, XIST, melanoma, MiR-139-5p, ROCK1